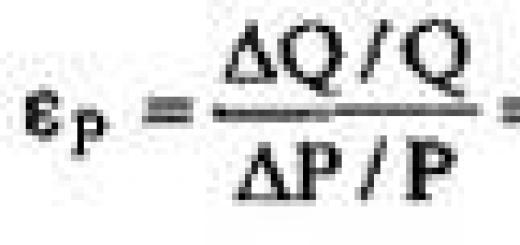Commodity credit ( English Trade Credit) is the most accessible and, consequently, the most common spontaneous source of short-term financing for an enterprise. In this case, the seller acts as a creditor, who provides the buyer with a deferred payment for the delivered goods. This source of short-term financing is usually the main source for small businesses, as they often find it difficult to attract traditional sources of debt financing.
Vendors tend to be the most loyal compared to other lenders. In this case, their motivation is to increase sales through softer credit policy. It should also be noted that its downside is the acceptance of a higher risk of buyer default.
Types of Commodity Credit Arrangements
Typically, a trade credit can be formalized in one of three types of arrangements.
- Open account ( English open account);
- Promissory note ( English Promissory note);
- Accepted trade bill ( English Trade Acceptance).
An open account is the most common type of trade credit agreement in which the buyer does not sign a formal debt obligation. Upon shipment of the goods, the supplier issues an invoice, which indicates the quantity of the goods, its cost and the date on which payment must be made. On the seller's balance sheet, this amount passes through the Accounts Receivable account, and for the buyer, through the account Accounts payable».
A promissory note is essentially a formal recognition of a debt obligation on the part of the buyer. In practice, a promissory note is most often issued when the due date for the open account, but the parties came to an agreement to extend the payment period. The features of this type of agreement are:
- longer payment term than an open account;
- this type of arrangement may involve the accrual of interest;
- the holder of the bill can transfer it to third parties, for example, sell it at a discount to the bank.
On the seller's balance sheet, bills of exchange are accounted for under the account "Promissory notes receivable", and for the buyer - under the account "Promissory notes payable".
An accepted trade bill is legally the most complex form of a commodity credit agreement. Before delivery of the goods, the seller issues a draft to the buyer ( English Draft) obliging the buyer to make payment on a certain date in the future. In this case, the seller will not deliver the goods until the buyer accepts the urgent draft ( English Time Draft). By accepting a time bill, the buyer indicates the bank in which the bill will be paid upon the due date. From the moment of acceptance by the buyer of the draft, an accepted trade bill is converted. The seller can wait for the date of payment and present it for collection to the specified bank, or sell it at a discount to third parties.
Terms of payment
It should be noted that the relationship of commodity credit between the seller and the buyer arises only when the goods are delivered on the condition of deferred payment. These payment terms include:
- Net period without discount. In this case, the seller does not provide discounts to the buyer for early payment. An example of such a condition could be "net 30", that is, a commodity credit is granted for a period of 30 days. Another example would be the condition “net 20, end of the month”, that is, payment must be made before the 20th of the current month.
- Net period with discount. This payment term requires grace period, during which the buyer can take advantage of the early payment discount. For example, the condition "3/15, net 45" says that the buyer will receive a 3% discount if paid no later than the 15th day, and must pay the entire amount if he makes the payment between the 16th and 45th days.
Formula
If the seller does not provide an early payment discount, then the use of commodity credit during the net period is essentially free for the buyer.
If the seller provides a discount for early payment, the use of trade credit will be free only during the period of the discount. If the buyer does not pay when it expires, the opportunity cost arises.
The effective annual interest rate of the opportunity cost of not discounting can be estimated using the following formula:
| r= | % discount | × | T | × 100% |
| 100 - % discount | Net credit period - Discount period |
where T is the time base for interest calculation (360 or 365 days).
Calculation example
To better understand the mechanism of opportunity costs, let's look at a simple example. Let's say that the seller delivered the goods on the terms "3/20, net 50" in the amount of $50,000. If the buyer pays on the 20th day, the buyer receives a discount of 3% or $1,500, that is, he will have to pay $48,500. If the buyer refuses from the rebate, he essentially receives a credit from the seller in the amount of $48,500, for the use of which he will have to pay $1,500 after 30 days.
Thus, the effective annual interest rate for the use of commodity credit will be:
| r= | 3 | × | 365 | × 100% = 37.63% |
| 100 - 3 | 50 - 20 |
If the buyer can raise financing at a lower effective annual interest rate, then the buyer should take advantage of the early payment discount. Otherwise, it will be more profitable to pay at the end of the net period.
Extending the term for paying accounts payable
As can be seen from the formula above, the cost of trade credit decreases as the difference between the net period and the discount period increases. Graphically, this dependence can be expressed as follows*.
* the chart was built for the payment condition "1/15, net X", where X varies from 16 to 45
If paid on the 16th day, the effective annual interest rate will be maximum and will be 368.69%. If the net period is 30 days, then this rate will be equal to 24.58%, and for a net period of 45 days it will already be 12.29%.
At the same time, in the first 15 days (the discount period), the use of a trade credit will be free, since the buyer does not have opportunity costs.
Advantages and disadvantages
The main advantages of using commodity credit are.
- Ease of attraction. The buyer does not need to conduct additional negotiations and sign an agreement, as would be the case with traditional lenders. Also, this type of agreement does not involve the provision of any collateral or additional security to the creditor.
- Flexibility. This form of ad hoc funding fulfills the matching principle most closely. In other words, the buyer receives financing for exactly the period and amount that he needs, which gives him an advantage over most other sources of short-term financing.
It should also be noted that for some enterprises this form of short-term financing remains the only alternative. This is especially true for small businesses or new companies that do not meet the requirements of traditional lenders.
However, when deciding whether to use a trade credit, the following disadvantages should be taken into account.
- High price. As a rule, the cost of this source of short-term financing is significantly higher than that of traditional sources such as, for example, Bank loan. This is due to the higher risk of non-payment and the absence of any collateral.
- Decrease in creditworthiness. As a result of the increase in the net period of lending, there is an increase in the balance of the Accounts Payable account, which, on the one hand, leads to an increase in current liabilities and a decrease in liquidity indicators, and on the other hand, to a decrease in turnover and solvency indicators. This can lead to problems obtaining financing from traditional lenders.
It should be remembered that a commodity credit, in principle, cannot be free of charge and its cost, as a rule, is included in the price by the seller. In other words, the price of goods on a non-deferred payment basis will almost always be lower than when selling on credit. This is because the seller not only recovers its increased financing costs, but also assumes the risk of the buyer's non-payment.
Thus, the use of commodity credit should be based on a compromise between liquidity and profitability.
In economic activity, sometimes there is a need for temporary borrowing not Money, but raw materials, seeds and similar things in kind. At the same time, the recipient is often interested in the stability of such relations, which a real loan agreement cannot provide. In such cases, a trade credit agreement is used. It provides for the obligation of the creditor to provide the other party not with money, but with things defined by generic characteristics. This is its main difference from the usual loan agreement.
A commodity credit agreement provides for the obligation of one party to provide the other party with things defined by generic characteristics. Commodity credit is intended to meet the needs of a person in the products of production and consumption, which at the time of the inclusion of the contract this person does not have.
Items transferred under a commodity loan become the property of the borrower. Commodity credit has a sign of repayment, characteristic of other loan obligations.
Since a trade credit agreement is concluded, as a rule, for production purposes, not only the rules on a loan (credit) apply to it, but also additional terms: on quantity, assortment, quality, packaging and other rules of the chapter on the sale of goods, unless otherwise provided by the loan agreement. The parties to the contract are any subjects of civil law.
A characteristic feature of a commodity loan is that its maximum amount is determined not only taking into account solvency potential borrower, but also based on the period for which it is planned to provide him with credit funds. At the same time, the deadline for granting a commodity loan usually does not exceed 5-7 years.
Commodity credit is provided to almost any capable citizen without security or with security of the borrower's obligations to repay the loan. The issuance of credit funds is made non-cash in any currency by crediting to the borrower's current account or credit card. commodity credit commercial banking
Repayment of a loan for the purchase of consumer goods with a deferred payment is made according to an annuity scheme, which provides for the monthly repayment of a part of the loan along with the payment of interest for using it.
Early lump-sum (or partial) repayment of the loan is allowed, however, in this case, the bank charges the borrower additional commission. In addition, at the request of the borrower, if there are good reasons, the bank can provide an installment plan to repay part of the loan for a period of 3 to 6 months, which, however, does not exempt the borrower from paying monthly interest.
If a major transaction is made and the buyer is given the opportunity to pay off it gradually, then it makes sense to draw up a trade credit agreement instead of a sales contract. This will help reduce the amount of VAT that must be paid to the budget from sales.
A commodity credit agreement provides that one firm (creditor) transfers goods to another firm (borrower) for a specified period. In this case, you will act as a lender, and your buyer will act as a borrower.
When this period expires, the borrower must return the same goods to the lender and pay interest on the loan. However, the buyer will not return the items to you. Therefore, when the due date approaches, enter into an agreement with him that the loan will be repaid in cash.
Otherwise, this agreement is subject to general rules about the loan agreement. This determines its consensual, reimbursable and bilateral nature, as well as the requirement that it be in writing. 3. Features of commercial and commodity credit
Features of a commodity loan
In economic activity, there is a need for temporary borrowing of raw materials, materials, seeds and other mass-produced goods under the condition of their return within the terms established by the contract.
At present, operations for the acquisition of property on the terms of a commodity loan are widely used. A creditor under a commodity agreement may be any legal or individual, and not just a bank or credit institution that has the appropriate license.
The lender, transferring the goods under a commodity loan agreement, the borrower also transfers the right of ownership to it. But in this case, the transfer of goods to the borrower is repayable, which is a characteristic feature of a commodity loan.
A commodity loan, like any loan, involves interest on the use of other people's funds.
A commodity credit agreement is a bilateral agreement: after its conclusion, both parties have both rights and obligations - one party acquires the right to require the other to issue goods on credit, that is, the creditor is obliged to provide credit in the form of goods. The borrower is obliged to accept the loan within the stipulated contractual period.
Legal regulation commodity credit agreements within the framework of §2 Ch. 42 of the Civil Code is reduced to two reference norms. According to the first of them, the rules on a loan agreement are applied under a commodity loan agreement, unless otherwise provided by the commodity loan agreement itself and does not follow from the nature of the obligation. The essence of the second reference rule aimed at regulating the commodity loan agreement is that the terms of the specified agreement on the quantity, assortment, completeness, quality, container (packaging) of things provided on credit must be executed by the parties in accordance with the rules on the agreement purchase and sale of goods, unless otherwise provided by the commodity credit agreement.
Thus, essentially the only hallmark commodity credit agreement, allowing to allocate it to separate view loan agreement, is the consensual nature of the commodity credit agreement.
At the same time, the consensual nature of a commodity credit agreement, which is a species-forming feature of this agreement, which makes it possible to distinguish it as a separate type of loan agreement, does not exclude the circumstance that all other general features of a loan agreement must be inherent in a commodity credit agreement. On the contrary, the absence of at least one of these signs does not allow qualifying the relevant legal relations as a commodity credit agreement.
A commodity loan agreement differs from a credit agreement in a number of ways. A commodity loan provides for the issuance of things with certain generic characteristics to the borrower, a loan agreement - money, that is, the object of a commodity loan is things other than money, and a loan agreement generates an exclusively monetary obligation.
The scope of the loan agreement is limited to the area of activity of professional creditors - banks and other credit organizations. In a loan agreement, only a bank or other credit organization that has a license to carry out banking operations, and any legal and natural persons can be in the commodity loan agreement.
These features are the main differences between the commodity loan agreement, otherwise it is subject to the general rules of the loan agreement, in particular, the conclusion in writing, the procedure for refusing to provide or receive a loan.
Features of a commercial loan
The obligation of commercial lending does not have the form of a separate contractual legal relationship, but arises in those civil law contracts, the execution of which is associated with the transfer of money or other things defined by generic characteristics to the ownership of the other party, provided that one of the parties to such an agreement provides its execution to the counterparty as if on credit, with a delay in the receipt of the counter-performance provided for by the contract by this counterparty. The latter, due to the above circumstances, for some time (until the fulfillment of his obligation) in fact uses the funds transferred to him by the other party or subject to transfer to the specified party in payment for goods received from it, work performed, services rendered. The legal relationship that develops in such situations regarding the use of other people's funds (things defined by generic characteristics) has the features of a loan type obligation and is called a commercial loan in the Civil Code.
E.A. Sukhanov emphasizes that the obligation of a commercial loan does not form a separate agreement, but is part of other civil law agreements. "A commercial loan is not an independent transaction of a loan type, but a condition contained in a reimbursable contract, he believes. - Any such contract, for example, a contract of sale, lease, contract, transportation, etc., may include a condition payment or advance payment for the property provided, the results of work or the provision of services, or, conversely, the deferral or installment plan of such payment.Economically, in all cases, we are still talking about a loan, essentially provided by one party to the contract, for example, when buying and selling goods with installment payment ".
As can be seen from the legal structure of a commercial loan, its legal significance is predetermined by the possibility of advance payment, prepayment, deferral or installment payment for goods, works and services. Any discrepancy in time of counter obligations under a concluded contract can be considered commercial lending, when goods are delivered (works are performed, services are provided) before they are paid or payment is made before the goods are transferred (works are performed, services are rendered).
In most cases, commercial lending is carried out without special legal registration by virtue of one of the conditions of the concluded agreement (on advance payment, on installments). For these purposes, the rule of paragraph 2 of Article 823 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation is formulated that the rules of the Chapter on the loan apply to a commercial loan, unless otherwise provided by the rules on the contract from which the corresponding obligation arose, and does not contradict the essence of such an obligation.
The rules applicable to a commercial loan are set out in Article 823 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation. Based on the text of this article, two important legal provisions follow. Paragraph 1 emphasizes the legitimacy of sales of goods on credit, advances to contractors and other forms of commercial credit. The second paragraph defines the range of rules applicable to commercial credit. According to this clause, the rules contained in Chapter 42 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation are applied to a commercial loan, unless otherwise provided by the rules on the contract from which the corresponding obligation arose, and if such application does not contradict the essence of this obligation.
The definition of a commercial loan, given in Article 823 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation, suggests that commercial loan- these are civil law obligations that provide for the deferment or installment payment for goods, works or services, as well as the provision of funds in the form of an advance or advance payment. That is, a commercial loan is a loan provided not under an independent loan obligation (loan agreement, loan agreement, commodity loan agreement), but in pursuance of contracts for the sale of goods, performance of work or provision of services.
Consequently, commercial lending is legally inextricably linked to the contract of which it is a condition. That is, a commercial loan is a payment condition contained in a reimbursable contract.
Article 823 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation lists typical cases of a commercial loan in its legal meaning: advance payment, advance payment, deferral or installment payment for goods, works or services. Any contract (for example, a contract of sale, supply, performance of work, provision of services, and so on) may include a condition on full advance payment or advance payment (partial payment) of the property provided, the results of work or services (established in the interests of the alienator or service provider) or a condition on the deferment or installment of such payment (serving the interests of the purchaser or service recipient). That is, a commercial loan can be conditionally divided into two types:
- 1) deferral or installment payment, provided by the seller of the property to the buyer, for which it is possible to receive remuneration as a percentage of the amount of the stipulated deferral or in the prescribed amount.
- 2) advance payment (advance) to the seller, for which it is also possible to receive remuneration.
Thus, the provision of a commercial loan implies that, under the terms of this agreement, each of the parties performs a dual role: the seller of the goods is both a creditor and the buyer is a borrower, or vice versa.
It should be noted that the contract for the "purchase and sale of goods on credit" or another contract that provides for the provision of a commercial loan, and the contract for "commodity credit" are different in their legal nature. Replacing one concept with another in a sales contract can lead to negative legal consequences.
It should be noted that the main difference between a commodity loan agreement and a commercial loan agreement is the materiality of the conditions stipulating the price of the goods and the terms for its return, in the absence of such an agreement, such an agreement will be considered not concluded. For a commodity credit agreement, these conditions are not essential. The indication of the price of the goods in the commodity credit agreement is advisory in nature, since the amount of interest payable to the creditor is calculated based on the contractual value of the goods.
Among economic entities, such types of lending as commodity credit and commercial credit are widespread. For example, in a situation where an organization temporarily needs raw materials, materials or goods, it can borrow them from another organization by entering into a commodity loan agreement. Commercial credit refers to such forms of lending as deferment and installment payment for goods (works, services), it also includes advances or advance payments for goods (works, services) by the buyer to the seller. The correct qualification of the contract has a great influence on the reflection of such transactions in accounting and reporting. Consider the main similarities and differences between commodity credit and commercial credit
24.05.2016Trade credit agreement provides for the obligation of one party to provide the other party with things defined by generic characteristics ( Art. 822 Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Execution commercial loan agreements associated with the transfer of ownership to the other party of monetary amounts or other things determined by generic characteristics ( Art. 823 Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
Any contract is considered concluded if the parties, in the form required in the relevant cases, have reached an agreement on all the essential terms of the contract ( Art. 432 Civil Code of the Russian Federation). At the same time, the conditions on the subject of the contract, the conditions that are named in the law or other legal acts as essential or necessary for contracts of this type, as well as all those conditions regarding which, at the request of one of the parties, an agreement must be reached.
To understand the main differences between the two types of contracts listed above, let's determine what conditions are essential for each of them.
Essential terms of trade credit and commercial credit agreements
A commodity credit agreement will be considered concluded if the subject of the agreement is defined, that is, the name and quantity of the goods transferred on credit. The conditions on the quantity, assortment, completeness, quality, container and (or) packaging of the items provided must be fulfilled in accordance with the rules on the contract for the sale of goods ( Art. 822 Civil Code of the Russian Federation). Thus, an essential condition for a commodity credit agreement is an indication of the name and quantity of the goods transferred on credit. The obligations of the borrower include the need to return the goods of exactly the same kind and quality, otherwise the contract may be qualified as an exchange contract. The price of the transferred goods is not an essential condition of the contract. The indication of the price of the goods in the commodity credit agreement is advisory in nature, since the amount of interest payable to the creditor is calculated based on the contractual value of the goods.
For a commercial loan agreement, an essential condition is the indication of the price of the goods and the timing of its payment, that is, the amount and conditions for granting a loan. However, the discrepancy between the timing of the transfer of goods and the timing of its payment is not always a sign of a commercial loan agreement. An analysis of numerous arbitration practices leads to the conclusion that commercial lending obligations do not arise automatically in advance payment for goods, but upon reaching an agreement on this (FAS ZSO post. No. F04-2871 / 2008 (4766-A45-17) dated May 15, 2008).
A similar conclusion that the discrepancy between the moment of receipt of the goods and the moment of its payment is not in itself a commercial loan (deferred payment for the goods), is also contained in other documents (FAS PO of April 15, 2014 No. F06-4575 / 13, of January 17 .2011 No. F06-12602 / 2010 in case A49-3817 / 2010, FAS SZO dated November 9, 2010 No. F07-9633 / 2010; determination of the Supreme Arbitration Court of the Russian Federation dated February 25, 2009 No. 1511/09).
Therefore, the advance payment granting a deferment and installment payments for goods, works or services constitute a commercial loan, if such payment terms are defined in the agreement as the provision of a commercial loan.
Differences in the forms of commercial loan agreements and commodity loans
In addition to differences in the essential terms of commodity credit and commercial credit agreements, it is also necessary to note the differences in their form.
From the analysis of norms chapter 42 of the Civil Code, it follows that a commodity credit agreement (to which the rules of paragraph 2 "Credit" of this Chapter apply) is a separate independent agreement, which is concluded in writing. Failure to comply with the written form will result in invalidity of the loan agreement. Such an agreement is considered null and void.
In turn, the provision of commercial credit is not independent legal deal. Really, Code defined ( paragraph 1 of Art. 823 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation) that contracts, the execution of which is associated with the transfer of money or other things defined by generic characteristics to the ownership of the other party, may provide for the provision of a loan, including in the form of an advance payment, advance payment, deferral and installment payment for goods (works, services ).
Therefore, the conditions for granting a commercial loan may be contained in the main contract (purchase and sale, provision of services, performance of work, etc.) or be provided for in an additional agreement to the main contract.
Compensation of commodity and commercial credit agreements
A commodity loan agreement can be either reimbursable, that is, it can involve the receipt of interest for the provision, or gratuitous.
AT code the possibility of concluding an interest-free (gratuitous) commodity credit agreement ( paragraph 3 of Art. 809 Civil Code of the Russian Federation): the contract is assumed to be interest-free, unless it expressly provides otherwise, in cases where, under the contract, the borrower is transferred not money, but other things defined by generic characteristics (the case of a commodity loan).
If the commodity credit agreement does not contain a condition on the payment of interest, the agreement is considered gratuitous.
A commercial loan agreement is always paid, except for the case when the agreement is concluded between citizens for an amount not exceeding fifty times the minimum wage established by law, and is not related to the entrepreneurial activity of at least one of the parties ( paragraph 3 of Art. 809 Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
If the terms of the agreement do not provide for the amount of interest for using a commercial loan, then the interest is calculated based on the refinancing rate on the day the borrower pays the amount of the debt or part of it*( paragraph 1 of Art. 809 Civil Code of the Russian Federation).
In addition to interest for the use of a commercial or commodity loan, the agreement may provide for penalties (forfeits) for violation of the terms of the agreement (The procedure for collecting penalties is established Art. 395 Civil Code of the Russian Federation), including for violation of the terms of the loan.
Penalties (forfeits) can be established both in reimbursable commodity or commercial credit agreements, and in a gratuitous commodity credit agreement. So, for example, when the parties conclude a gratuitous trade credit agreement in case of violation of the essential terms of the agreement, the borrowing party will have to pay penalties if there is a condition for the payment of a penalty in the agreement.
A reimbursable agreement on a commodity or commercial loan may simultaneously provide for both interest for using the loan and penalties (forfeits) for violation of contractual terms.
Businesses often pay each other with commercial credit. Thus, it is more convenient for each company to attract borrowed funds than to extract its own money from circulation. This method is especially relevant for small firms that simply do not have their own savings, so for development they need to attract funds from banks or third-party organizations. A commercial loan is considered an actual way out of a difficult situation, and it is presented in several forms. It sets a variety of rates and conditions, so you should have a good understanding of the rules for registration in order to guarantee the effectiveness of the use borrowed money.
concept
Although it is considered a loan, it has many specific features:
- do not issue state or commercial banks loans of this type, since firms cooperate with each other for this, therefore, an intermediary in the form of a banking institution is not involved;
- no special license is required for such a process;
- such a transaction does not act as a separate process, therefore, a special agreement is not drawn up for it, since only an additional agreement is formed to the main contract;
- companies and enterprises themselves act as lenders and borrowers;
- it is allowed that the participants were natural persons or individual entrepreneurs.
Loans provided by commercial banks are not considered commercial, as they are presented in monetary terms. When an appropriate agreement is drawn up between enterprises, the loan is usually presented in a commercial form. Under such conditions, the transaction is an addition, so a simple written form is suitable for its expression.
How is it different from bank loans?
A commercial loan is a transaction, the parties to which are different firms that do not have a banking license. It can be provided by both the seller and the buyer, so it can be expressed in the form of installments, deferrals, advance payments or prepayments.
A commercial loan has many differences from a standard loan that is offered banking organizations.
| Criterion | Commercial loans | Bank loans |
| Creditor | Different legal entities, individuals or individual entrepreneurs who enter into various contracts with each other involving the supply of goods | Only banking institutions with the appropriate license |
| Submission form | Commodity | Monetary |
| Interest rates | Low, ranging from 3 to 15 percent | High, and for different loans they can even reach 50% |
| Loan fee | Included in the price of the goods | Determined as a fixed or floating percentage, which depends on the amount of the loan |
Thus, commercial banks provide loans that are significantly different from a commercial loan, so these concepts should not be confused.
Forms of commercial credit
It can be presented in different forms, each of which has its own characteristics. A specific form is negotiated in the process of forming a contract between companies. At the same time, it is decided what will be the procedure for granting a loan, what tariffs and other conditions of a commercial loan will be established. In most cases, such a process is formalized in the form of an additional agreement to the main contract.
If the main contact is formed in writing, then the contract for a commercial loan is made in the same form. The same applies to the registration of documentation.

Forms of commercial credit are numerous, but most often presented in the form of:
- Prepaid expense. It is a partial payment that is made by the buyer, so he acts as a creditor. Based on the terms of the contract, he pays the full cost of the goods before the direct receipt of the goods. The credit period starts from the moment when the advance payment is transferred, and ends on the day when the buyer receives his goods.
- Prepayment. Based on the terms of the agreement, the buyer pays in full for all goods in advance, so he is also a creditor. Prepayment implies that services are provided or goods are shipped some time after the seller receives the money. Therefore, the loan term can vary significantly depending on the conditions specified in the contract.
- Postponement. The provision of this form of commercial credit involves the seller shipping goods or providing a service, and payment for them will be received by him later. It can be represented by several transfers of money or one large payment. The time when funds should be transferred is stipulated in the contract in advance. The creditor is the seller, so he can demand the timeliness of the return of funds. If this condition is not met, then fines are charged on a commercial loan. They can be stipulated in the agreement or calculated on the basis of the size of the refinancing rate.
- Installment. The creditor is a seller who wants to sell his goods, so he agrees that they are paid not in full, but in part in equal payments. A special schedule is drawn up, on the basis of which the buyer must pay for the goods.
Thus, commercial credit can be presented in different forms, and also it is provided in different ways. Each method has its own characteristics, so it should be studied by sellers and buyers separately.
Promissory note credit
It is considered the most popular method of providing a commercial loan. For calculations, a written obligation is used, in which the exact amount of a commercial loan is prescribed. It is these funds that must be provided by the borrower to the lender.

Various bills of exchange can be used to use this loan method:
- Solo bill. It is called in another way simple, and at the same time, its use requires that two parties take part in the transaction. A specific period is set, at the end of which the drawer, who is the borrower, pays the amount specified in the agreement to the creditor. Typically, such a bill is used for domestic settlements.
- Draft. Such a bill is called a bill of exchange. It assumes that an additional third party is involved in the transaction. The drawer, who is the creditor, indicates to the drawee, represented by the borrower, when the goods under the contract must be paid for in favor of a third party, called the remitter. Typically, such a bill is used for interstate settlements. The recipient under such conditions is the exporter's bank.
Thus, it is optimal for Russian companies to use a promissory note to arrange a commercial loan.
Factoring and forfaiting
Factoring is a popular form of commercial lending. It consists in the fact that a bank or a special company collects accounts receivable other client companies. The firm buys back the debt from another creditor to whom it is originally due required amount. But at the same time, he receives only a certain part of the amount, and the remaining funds are transferred as soon as the money is received from the debtor. Sellers resort to this method if the debtors do not return the funds on time, therefore, due to the efficiency of receiving money, they can use it for development or use it in circulation.
Forfaiting is a form of factoring, but the difference is that on-lending is implemented in foreign trade relations, and a bill of exchange is also required.
Leasing
This type of commercial loan is becoming more and more popular with Russian organizations. It consists in the fact that certain real estate, vehicles or other valuable property is transferred to a long-term lease to another person. At the same time, it remains possible to redeem this object in the future, for which a residual value is established.
The most frequently issued leasing for the acquisition of:
- properties that are residential or commercial;
- Vehicle;
- equipment necessary for the operation of a particular organization.
With such a loan, purchases are made for a leasing organization that acts as a creditor for the end user of the equipment. An agreement is necessarily concluded between the two participants, which specifies the procedure for granting leasing, as well as the time frame when the subject of the agreement can be redeemed.

Consignment
It is considered a common form of commercial credit among Russian entrepreneurs. In another way, such a process is called "goods for sale." The procedure is that the owner of the object, who is the consignee, provides the consignee, represented by an intermediary, with a specific product. It is further sold to the final consumer.
The intermediary pays for the goods not immediately, but after the sale. If it is not possible to sell the goods, then it is returned to the manufacturer, so it is considered that the transaction did not take place.
This method is used in a situation where a new product is supplied to the market, so there are doubts among sellers that it will be in demand.
Open account
Such commercial credit is used by companies that have good and long established relationships. It lies in the fact that certain batches of goods are systematically delivered to the buyer, and at the same time a deferred payment is provided.
Such a transaction does not require documentation for each delivery, but it is agreed in advance what the maximum limit of the resulting debt is. If the invoices are not paid by the buyer in a timely manner or the goods are not provided, then this is a violation of the contract. For this, a penalty is charged, and the commercial loan rate may be prescribed in the agreement or may be calculated based on the refinancing rate that is set at a particular point in time.

Discounts for paying on time
Suppliers of goods can motivate buyers who make timely payments for delivered goods. At the subsequent signing of the contract with such a client, suppliers offer discounts.
The main condition for using such a commercial loan is the need for timely deposit of funds by buyers.
Seasonal credit
This lending option is used only by enterprises operating in the seasonal business sector. To do this, the seller sends the goods to the buyer in advance, which allows the recipient to form optimal stocks before the sale or the season.
Goods are paid after the end of the season, when the debtor receives the necessary funds for this.
The advantages of such lending for the seller include the possibility of saving on warehouse rental, and the buyer receives a deferred payment.
Board size
Commercial loans are practically not regulated by Russian law in any way. Since it is possible to use goods or money for a certain period of time, a payment for such a loan is required.
The commercial loan rate is much lower than bank interest, so using this method is considered a profitable process for every firm. It remains unchanged in the process of cooperation between companies.
Interest on a commercial loan is usually set in the agreement itself, drawn up between the two parties. This takes into account some important points regulated by the market itself:
- the rate must be lower than in a bank or other credit institutions because otherwise this method of lending will not be attractive to companies;
- the payment must cover the costs of the creditor, otherwise it would be inappropriate to provide goods or funds;
- payment for credit should not lead to the fact that the competitiveness of goods decreases.
It is allowed to additionally indicate the amount of penalties and fines in the contract if the main points are violated this document. For this, direct interest on the established loan amount can be prescribed, and if such information is not available, then information from the legislation is used, therefore, the size of the Central Bank refinancing rate is taken for calculation.

Deadlines and penalties
With long-term cooperation between companies, there may not be a fee for using a commercial loan, so interest is charged only if the terms of payment or delivery of goods are violated. In this case, interest acts as a penalty for non-compliance with the terms of the contract.
Typically, a commercial loan agreement does not set strict terms, so there are some periods of time.
pros
The positive aspects of such a loan include:
- can be obtained without a bank loan desired goods without payment or receive payment for goods not yet shipped;
- the lender increases turnover if he is a supplier;
- the buyer can lay low interest for such a loan in the cost of goods;
- enterprises support each other with the help of such an offer;
- firms maneuver their capital;
- reduced need for standard bank loans.
Due to competent and official registration, it is possible to recover funds from the borrower forcibly through the court.

Minuses
A commercial loan has not only advantages, but also some disadvantages:
- limited by the supplier's inventory or the borrower's solvency;
- due to regular changes taking place in the market, it is not always advisable to use such an offer;
- product prices are constantly changing, and at the same time, the buyer, having paid for a large consignment of goods, will no longer be able to change his mind;
- the borrower can always declare himself bankrupt, so the lender can lose his funds;
- there is a possibility that the parties will not perform the terms of the contract in good faith.
Thus, commercial credit is provided by companies that do not have a banking license. It can be presented in different forms, so the option that is ideal for specific organizations is selected. The amount of the fee is set by both parties, but it is always less than the interest on bank loans. Such a loan has both pros and cons, so each company must carefully evaluate the effectiveness and feasibility of such a contract.