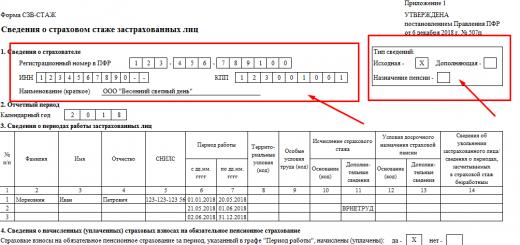
For all citizens on the territory of Russia, the law provides for a mandatory health insurance. Each person becomes the owner of the CHI policy, on the basis of which he has the right to guaranteed medical care. But not everyone knows what range of services is included in this program. Many citizens, even presenting an insurance policy at a polyclinic, today face a refusal to provide medical care of one kind or another. And not everyone is ready to defend their rights. Often this is due to a low level of public awareness about what guarantees each A5 blue sheet or progressive plastic electronic card, and for what volume of services the owner of one of these documents can apply. We will talk about this in this article.
The essence and purpose of the CHI policy
A compulsory health insurance policy is an official document that is designed to certify the right of the insured person to receive medical care free of charge in the amount provided for in the basic CHI program. The functions of the policy, as well as its guarantees, are determined by the Law of the Russian Federation “On Compulsory Medical Insurance in Russian Federation» No. 326-FZ, adopted on November 29, 2010.
Under the terms of the above normative act, the policyholder must have it with him at all times in order to take advantage of the opportunity when insured event receive free medical services in the required volume. Art. 16 of the law provides that, in the absence of insurance policy a citizen can only count on emergency assistance. The insured has the right to use the document in the medical institution to which he is attached according to his document.
Medical care for compulsory medical insurance policy is carried out for citizens absolutely free of charge and is financed from the funds of insurance funds - territorial and federal, which accumulate their funds from the regular contributions of insured persons. For the employed, such contributions are made by their employers from the wage fund, and for the unemployed - by the state. As a result, the entire population of the Russian Federation, regardless of age, gender, type of employment, social or material status, has the right to care in medical institutions in equal volumes and of the same quality.
The policies of the new model, the issuance of which started in 2011, are of an indefinite nature, i.e., they will be valid throughout the life of the owner, and when changing the workplace, it will not be necessary to replace them. Also, the law discussed above saved the new document from being tied to the place of residence of a person - the medical policy became valid throughout Russia. More detailed information about the procedure for registration and types of documents can be found in the articles:
What rights and guarantees does the policy provide to its owner?
Each insured citizen has the right to receive only one copy of the document, which only he himself can present. Attempts to use someone else's personal data are classified as offenses and are punishable by law. The medical insurance policy provides for the following rights and guarantees for insured citizens:
- Receiving free medical care within the territorial borders of Russia: during your stay within your permanent place of residence - on the basis of regional program compulsory medical insurance, and outside it - according to the federal program of compulsory medical insurance;
- Implementation of the choice of an insurance medical organization (state clinic, private center, etc.) among those institutions that participate in the implementation of the CHI program;
- Attachment to a medical institution not by registration, but by actual place of residence (if they differ);
- Change medical institution in connection with the move (unlimited number of times) or for personal preferences (no more than once a year);
- The choice of the attending doctor by submitting an application addressed to the management of the medical institution;
- Obtaining complete and accurate information about the volume, quality of medical care within the framework of regional and federal CHI programs;
- Privacy and protection of personal data;
- Compensation for damage by a medical organization as a result of its failure to fulfill its obligations to the insured person;
- Protection of personal rights in the field of CHI.
If the owner of the compulsory medical insurance policy is faced with the refusal of health workers to provide him with the necessary medical services, with the provision of poor-quality, incomplete or untimely assistance, the law of the Russian Federation "On Compulsory Medical Insurance in the Russian Federation" provides for the right to file a complaint against the specified clinic. It can be addressed both to the management of the insurance organization that issued the document, and to the territorial or federal compulsory health insurance fund.
Loss or damage to the policy does not entail a complete loss of the citizen's right to legally guaranteed free medical care. In such cases, a person should contact insurance company for . Until that moment, he will be issued a temporary document (for one month), allowing him to use medical services in the same volume.
What medical services can be obtained under compulsory health insurance?
The owner of the CHI insurance policy has the right to receive free of charge only those medical services that are provided for by the content of the regional and federal CHI program. Surcharges can be requested from a citizen only if the amount of medical care necessary to save his life or maintain his health exceeds the base provided by the policy. The CHI policy includes the following assistance:
- Emergency, which is an emergency medical care necessary to eliminate the threat to human health and life;
- Outpatient, which is provided in a polyclinic and provides for diagnostic procedures, scheduled medical examinations, treatment of diseases at home or in day hospitals. According to the CHI program, outpatient medical care does not include free provision of medicines to citizens during treatment;
- Inpatient, which turns out to be in the form of planned and emergency hospitalization in such cases as pathologies or termination of pregnancy, childbirth, exacerbation of chronic ailments, referrals to polyclinics, situations associated with the need for intensive care.
In addition to these types of services, the CHI policy guarantees its owner the opportunity to use medical care associated with the use of modern high-precision technologies and techniques - both for the purpose of conducting a study for diagnosis, and directly for treatment (with the exception of cosmetic, plastic surgery). The document of the insured person also provides that its owner can become a participant in preventive, rehabilitation, health-improving, informational activities organized by doctors as part of educational work with the population. For privileged categories of the population, it is also necessary when receiving free medicines.
For which diseases can you get free medical care?
The Law of the Russian Federation on Compulsory Medical Insurance provides for a wide list of diseases for which the policyholder can receive free diagnostics and therapy. Turning to the health care institution to which he is attached, he will need to present a document at the registry. Free medical services can be obtained at:
On a free basis, the holders of the CHI policy undergo routine vaccination, as well as annual fluorography. Having a document, once every three years you can take the opportunity to undergo examinations and a medical examination within the framework, as well as be under dispensary observation, call a doctor at home, and undergo other free procedures provided for by law.
On the territory of the Russian Federation, a compulsory medical insurance policy can be issued not only to residents with Russian citizenship, but also to foreign citizens, stateless persons, and those with refugee status. All categories of the population are entitled to equal service in medical institutions. The only difference between the documents is their validity period: if for Russian citizens they are indefinite, then for persons temporarily staying on the territory of the Russian Federation, they are considered valid until they leave the country.
Conclusion
The CHI policy is issued to the insured person after the conclusion of an agreement with the insurance medical organization. This document is proof of the right to receive free medical care under the current program of state guarantees. Guarantees provided by the state for policyholders make it possible to cover the most vulnerable categories of the population with qualified assistance, for whom it would otherwise be inaccessible.
Since 2015, established two limit values of the base for calculating insurance premiums:An employee of Svetly Put LLC from the beginning 2015 year, a salary in the amount of 680,000 rubles was accrued.
1) for the PFR - 711,000 rubles.
2) for the FSS - 670,000 rubles.
At the same time, he also performed work under a work contract, the amount of remuneration for which amounted to 70,000 rubles.
We will determine the basis for calculating contributions to each fund and the amount of contributions itself. FIU.
Contributions to the PFR at a rate of 30 percent are subject to employee income not exceeding 711,000 rubles.
In excess, that is, from an amount equal to 39,000 rubles. (680,000 + 70,000 - 711,000), contributions must be paid at a rate of 10 percent.
In total, pension contributions in the amount of 217,200 rubles will be accrued. (711,000 rubles x 30% + 39,000 rubles x 10%). FFOMS.
Contributions are levied on all payments in favor of employees.
That is, the base for this employee will be 750,000 rubles. (680,000 + 70,000).
The amount of contributions will be equal to 38,250 rubles. (750,000 rubles x 5.1%). FSS.
Payments under a civil law contract are not included in the base of contributions to the FSS.
That is 70,000 rubles. are not subject to fees.
Exceeding the salary limit in the amount of 10,000 rubles is also not subject to contributions. (680,000 - 670,000).
The accrued amount of contributions will be 19,430 rubles. (670,000 rubles x 2.9%). Injury.
Limit for the Social Insurance Fund = 670 thousand rubles. NOT applies to injury contributions
(These contributions are paid from all payments, as before, there are no restrictions for them).
Payment of contributions to the Pension Fund of the Russian Federation and for honey. insurance is mandatory for all employers and entrepreneurs. To transfer health insurance premiums, you need to know the BCC and the interest rate. In the article, we will consider what are the rate and percentage of deductions in the FFOMS.
How to calculate the installment rate
Most employers calculate the FFOMI rate at the current rate of 5.1%. There is no maximum amount set for these premiums. Regardless of how much the employee earned in a year, a deduction for honey must be made from each payment. insurance. Contributions depend on the minimum wage, so the calculation is not difficult.
On the example of IP contributions for "himself" consider the amount of compulsory insurance in 2017:
- Pension - 7,500 * 26% * 12 = 400 rubles.
- Honey. insurance of merchant contributions - 7,500 * 5.1% * 12 = 4,590 rubles.
So, insurance premiums for merchants who pay for themselves, amount to 27,990 rubles in 2017. This amount is usually divided into four quarters. At the end of the quarter, merchants are required to pay a single contribution in the amount of 6,997.5 rubles. The monthly rate is 2,332.5 rubles.
Knowing the annual amount, these contributions can be paid both in a single payment and quarterly. Almost all merchants make quarterly payments. They are fixed for entrepreneurs who do not have employees. For all employers, the insurance premium and its rate depend on the chosen taxation system, on the amount that was accrued to the employee during the year.
Insurers who have employees, make deductions at the following rates:
- PFR - 22%. This amount varies and depends on the danger of work at the enterprise. Additional contributions may be established, about which the fund informs the head in a separate notice.
- FSS - 2.9%. Contributions are charged for danger and injury. The amount of this contribution is determined for each enterprise separately.
- FFOMS - 5.1%.
If the company is on a simplified system and at the same time is engaged in a “preferential” type of activity, then the amount of the insurance premium will be different.
To use the preferential contribution, you need to check whether the economic activity code refers to the “beneficiaries”, the list of which was established on the basis of Federal Law No. 212. For such companies and entrepreneurs, contributions to the PFR are 20%, and insurance premiums to honey. fear 5.1%.
If the pension contribution can reach the limit and decrease, then the medical rate has no limit, so the 5.1% deductions are valid for the whole year.
Contribution rate to the FFOMS in 2017
The changes that will affect all taxpayers in 2017 are, first of all, the transfer of powers from one regulatory authority to another. Now they will be engaged in checking the correctness of accrual and payment tax authorities. the federal law now it will not act, it will be replaced by NK.
Checking the activities of entrepreneurs and organizations will be carried out on the basis of new legislation. This is the only and main change in 2017. What percentage of contributions to the FFOMS we expect can be seen in the table:
As we see insurance rates will not change and will remain the same. The regulatory authorities have not canceled the reduction in contributions, just now not all employers will be able to take advantage of it. Changes in the size of the insurance premium will be felt by the merchants who paid for themselves.
An increase in the minimum wage by 7,500 rubles will lead to an increase in the amount of taxes on compulsory insurance.
Who does not pay dues
Who can not pay dues? These include:
- Pharmacies, merchants licensed to carry out pharmaceutical activities.
- Organizations involved in the field of social services to citizens.
- Charity organisations.
- R&D companies.
For these organizations, a tariff rate of 0% is provided.
The following insurers can use the 4% rate for the calculation of insurance mandatory contributions to the FFOMS:
- Information technology companies.
- Businessmen and organizations that are engaged in inventions and scientific developments.
- Tourist organizations.
In this way, interest rate to pay the contribution directly depends on the type of activity of the entrepreneur and organization. As far as the structure is active in state and charitable financing, the rate of contributions also decreases.
The overwhelming majority of citizens of our country restore their health using the possibilities of the system of compulsory medical insurance (CHI). Examination by specialists, medication, dental treatment, and so on have become familiar realities of our days. But CHI provides an opportunity to carry out more responsible medical interventions, including surgical ones, free of charge. You will learn how to make an operation under the CHI policy below.
What operations can be done under the CHI
Periodic changes are made to the list of free surgical operations aimed at expanding the ability of citizens to restore health through surgical intervention. An updated list of free operations is sent to medical institutions and insurance companies registered under the MHI. The information is public.
Free access is provided by placement on the information stands of medical institutions, their websites, as well as informing, at the consultations of the attending doctor, which operations are performed free of charge.
The list of free operations under the MHI policy for 2020 includes the following interventions:
- Surgical operations on the eyes:
- with cataract of the lens of the eye;
- intervention for strabismus, including strabismus in children;
- traumatic deformation of the retina;
- glaucoma;
- detection of congenital anomalies.
- Sentoplasty (correction of the nasal septum), with the following indications:
- impaired respiratory function;
- lack of smell;
- swelling of the mucosa;
- not resistant to SARS;
- not standard breathing, snoring;
- excessive dryness of the sinuses, systematic pain.
- Removal of the gallbladder in the presence of cholecystitis, functional disorders (cholesterosis, gallstone manifestations).
- Operation Marmara (diseases of the veins of the organs of the reproductive system of men) with indications:
- varicocele of the second and subsequent stages;
- impossibility of fertilization (sperm excretion);
- painful sensations;
- aesthetics;
- scrotal tissue changes.
- Joint arthroscopy.
- Operations on the veins in venous diseases.
- Diseases of the field of gynecology.
- Thoracic (oncology, pathological changes in the lungs).
- Stop valgus.
The presented list is not a complete list of gratuitous surgical interventions that are permissible, in the presence of a compulsory medical insurance policy. However, cosmetic interventions (for example: bariatric surgery) are not included in free medical care.

Who can get free health care
All categories of citizens who have concluded compulsory medical insurance agreements in accordance with the established procedure are entitled to receive free assistance in the country, including:
- having labor relations with enterprises, organizations in the sphere of production, consumption and distribution of material goods;
- receiving funds or remuneration under licensing, scientific, publishing alienation agreements;
- private entrepreneurs and other categories providing for themselves independently;
- leaders and participants of farm enterprises;
- community members involved in folk crafts and tribal economic activities;
- citizens who do not have a job (children under the age of eighteen, adults on pensions, teenagers who are in training, the unemployed, a guardian of a child under the age of three, caring for a disabled person of the first group or an adult over the age of eighty)
- military personnel, employees of special organizations, including medical workers;
- foreigners legally staying on the territory of the country and engaged in labor activities, within the limits permitted by the regulatory legal acts of the state;
- persons who, in accordance with the established procedure, have received the status of refugees.
Institutions of the Ministry of Health do not have the right to refuse to provide emergency free medical care, including specialized, to persons who have not concluded an MHI agreement or with missing information about their policy on a single database of the MHIF.

Where can I get treatment for free
The above categories of citizens have the right to receive free medical care under compulsory medical insurance throughout the country, regardless of the presence of registration at the place of residence, place of stay or lack of such, at the time of application.
In relation to the category of medical care related to the conduct of planned surgical interventions, the insured person has the right to choose any specialized medical institution in Russia, in his opinion, capable of performing the operation with the best results. At the same time, the medical institution must, in accordance with the established procedure, participate in the MHIF system.
Medical institutions (hospitals, clinics and others) become participants in the system after concluding a cooperation agreement with the CHI. If there is a quota, they cannot refuse the possibility of performing an operative intervention if the operation is indicated.
It should be remembered that the length of the waiting period for a planned operation in another region, as well as at the place of residence of the patient, can take a significant amount of time. This is due to the strict quota of operations, due to the significant financial costs of its implementation, as well as the large number of patients who apply.
When choosing a medical institution for a planned operation, the following should be considered:
- the insurance coverage covers only the operation;
- the quality of the work of practicing surgeons is approximately equal, both in polyclinics of the capital regions and local medical institutions, where in the first case the operation is accompanied by the most advanced equipment, in the second - experience in performing multiple operations;
- waiting time for free operation, where big cities it may take long time(up to a year or more), for which side effects can be provoked, while waiting for local surgery will take up to the next few months;
- the cost of paying for services not covered by compulsory medical insurance.
Of no small importance is the opportunity to consult during postoperative rehabilitation with the surgeon who performed the operation. If the medical institution is located at a considerable distance, additional cash costs are expected.

How to make an operation under the CHI policy for free in steps
Obtaining surgical care under compulsory medical insurance coverage is a simple procedure that includes the following steps:
- Visiting the attending doctor in the attached medical institution. The field of study of analyzes and examination of the patient, he evaluates the indications for surgical intervention. If they are available, the doctor is obliged to write out a referral to a specialized clinic. The patient has the right to declare his referral for surgery to a pre-selected medical facility.
- After receiving the referral, the patient is registered for an appointment for a consultation at the selected institution. Registration is carried out by personal visit or in another manner provided by the hospital.
- Arrive at the appointed time to the hospital doctor for paperwork and consultation. Provide him with a referral, an identity document, an insurance contract (policy), the results of the study and medical card. The doctor decides on the need for admission to the hospital. Explains what is free and what you have to pay for.
- The decision to place, for the duration of the operation in the hospital, is accompanied by additional studies of analyzes.
- Within ten working days, the patient is notified of the date of the surgical intervention.
- On the appointed day, the patient is hospitalized.
About the quota. They are determined depending on the financial ability of the MHIF, territorial departments of the regions, to compensate for the expended consumables, the work of specialists and personnel during a certain number of surgical operations.
State medical institutions participating in the MHI system purchase medicines, medicines, equipment for surgical operations within the framework of the funding. Procurement is carried out on the basis of the organization of tenders. Where is the determining factor. The final delivery price is shown. Thus, when performing CHI operations, one should not count on advanced models of endoprostheses and other things.

Do I need to pay extra for services?
Surgical intervention according to compulsory medical insurance is free of charge. It includes: direct operation, anesthesia (if necessary), consumables, use of specialized equipment. The requirement of the institution for additional payment is not legal. But the patient independently finances travel to the place of the operation and back, preoperative accommodation outside the medical facility. The possibility of providing additional opportunities for compensation is allowed in relation to the receipt of services not included in the list of the CHI system, including:
- conducting anonymous diagnostics at the request of the patient (excluding HIV);
- manipulations carried out with a visit to the patient at home (diagnosis, consultation, medical treatment), with the exception of the physical impossibility of the patient to come to the medical facility for this;
- diagnostics and medical procedures for sexual pathologies;
- speech therapy activities of the adult population;
- vaccinations, with the exception of those provided for by compulsory medical insurance;
- post-operative measures, including sanatorium, if they are not provided for by the insurance program;
- cosmetic procedures;
- prosthetics of the oral cavity, with the exception of the cases provided for by compulsory medical insurance;
- psychological support of the patient;
- methodological measures for familiarization with patronage, provision of first aid and the like.
Medical institutions that provide, along with free, paid services, are obliged to inform about their existence by posting lists and price lists on the reception stands. At the same time, when deciding on hospitalization, the patient is personally acquainted with paid opportunities to improve the conditions of stay in the inpatient department of the hospital.
The insured person has the right to contact the insurer or the MHIF to clarify the legality of claiming additional funds while in a medical institution. Paying for certain services and drugs.

What to do if you are denied treatment if you have a policy
The low awareness of the population about their rights to medical care under compulsory health insurance often leads to conciliation in case of an unreasonable refusal to provide medical care or claiming additional money for procedures, including surgical operations. The situation is changed by the opportunity to get acquainted with the conditions, procedure and list of services on the official websites of the Ministry of Health and FFOMS.
Establishing the fact of a violation should be accompanied by measures to protect personal rights, including appeals:
- Management of the medical facility.
- District (city) health department.
- An insurance company that accompanies the MHI agreement.
- Territorial subdivision of the MHIF.
- Federal Office of OMS.
- Commission expert arbitration.
- Judicial authorities.
A statement of violation of the patient's legal rights in the provision of compulsory medical insurance coverage is drawn up in a businesslike, discreet style and contains:
- information about the person whose rights have been violated;
- information on the conclusion of an insurance contract (policy);
- details of the medical institution that refused to provide medical care, or committed other violations;
- the period of medical procedures or improper maintenance in hospital treatment;
- the course of events, the circumstances that forced the patient to spend personal cash, their volume.
The application is accompanied by the medical and financial documents necessary to prove the violation (extracts from the history, checks for paying for medicines, etc.).
You will learn more about how the system works and how to get a new sample below.
We are waiting for your questions in the comments.
For free legal advice, you can apply right now on our website. Just fill out the form.
Please rate this post and like it.
This article will discuss such a concept as "payments for insurance" for compulsory medical insurance and the stages of their payment, what changes have occurred this year.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to solve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and IS FREE!
A person is constantly faced with medical care, which takes him a lot of finances. The best option compensate for the costs - insure.
All individuals in Russia have the right to free healthcare. An insurance policy will help with this. How to apply for it, what is needed for this, whether it is necessary to pay contributions and what is their size - more on that later.
Basic Information
Faced with the concept of "insurance for medical care", many do not know what it is, why it is necessary to issue a policy. It is necessary to understand this term.
What it is
Insurance means the creation of a fund from which funds are allocated for medical treatment.
In this case, the insurer must pay contributions. Since the concept has a probabilistic nature, not everyone will need an insured event.
There is a possibility of redistribution of risks among the insured - a contribution can be made by one person (the insured), and another person (the insured) can use the funds.
There are also disadvantages of insurance:
The amount of the deposit depends on the profit of the insurer, and the guarantees for the provision of medical care are the same for everyone.
The MHI policy guarantees that a person in trouble will be able to use free medical care in any region of the Russian Federation.

The insured may have only one policy, which is in his hands. The insurance organization is obliged to familiarize the insured persons with the rules and obligations.
Who needs it
Medical insurance - protection of the individual and her health. Being in another country, treatment without a policy will be expensive, and they may even refuse medical care.
Depending on the age of the person, the type and complexity of the disease, the price of the policy will be different. CHI insurance policy is required for the following categories:
Whether a person works or not - insurance does not depend on this, this service is mandatory.
To obtain a policy, you must visit an organization that deals with insurance (CMO) and provide it with documents (persons under the age of 18 are not eligible, as they are considered incompetent).

For minors, insurance occurs in those HMOs in which parents are served or by law.
If the application is not provided by the person himself, but through a representative, then it is needed. Package of documents:

Legal regulation
The population of Russia has the right to the protection and protection of their health. This includes the provision of medical and social assistance, favorable working conditions, and health improvement.
Health care is carried out regardless of gender, race, nationality or language. Together with legal citizens of Russia, foreigners (who live on its territory) and refugees also have this right.
In case of illness, loss of legal capacity, a person must be provided medical care any type.
For example, preventive measures, diagnostic) and social measures, that is, care for the sick, payment of disability benefits.
Also, the population of the Russian Federation has the right to free medical care in health care systems - state type or municipal.
Compulsory medical insurance for the working population is an innovation. It guarantees equal rights for all segments of the population in the provision of medical care.
The basic program includes:
- help with acute chronic diseases;
- life-threatening situations;
- ambulatory treatment;
- home diagnostics;
- preventive measures: vaccinations, examinations;
- hospital treatment;
- dental assistance.
Frequently asked Questions
For people making contributions for the payment compulsory insurance for medicine, there are a lot of questions. Let's consider the most frequent ones.
Exemption from payment
This benefit is used by organizations of the disabled ().
Also, no payment is charged to the Compulsory Medical Insurance Fund (during the election campaign) for:
- funds of candidates for local authorities;
- income received from the election campaign by members of the commission.
Such a decision can only be made territorial fund oms().
To consider the issue, you need to provide an application for exemption from paying fees and photocopies of documents - a certificate of registration of the organization.

Nuances for IP
Self-employed individuals pay their own health insurance premiums. The calculation takes place at a standard rate, taking into account the minimum wage.
To calculate the contribution, it is necessary to multiply the minimum wage by the tariff and the number of months for which the contribution is paid as an individual entrepreneur. In 2020, the minimum wage is 5965 rubles, that is, the contribution is 3650.58 rubles.
Starting from this year, the amount is not rounded, but paid in kopecks. Individual entrepreneur the right to make a contribution in installments or all at once for a year. There is no need to report to any organization for this.
An entrepreneur has a choice - in addition to the general taxation system, special ones can be used (subject to the conditions of this regime).
Choices:
A contribution of 1% (additional) is added to the budget of the FFOMS to the established amount if the entrepreneur's income is more than 300,000 rubles per year.
For example - the profit amounted to 400,000 rubles, which means that the DP is calculated as follows - (400,000 - 300,000) * 0.01. this amount should be paid for health insurance.
- Taxes may be less than the amount of the contribution that was paid for a certain period.
- The due date of the fee may reduce the amount of the fee. That is, if you pay immediately by quarters, you can count on a smaller amount.
- The additional contribution also affects the reduction in the amount of tax.
- If the simplified tax system and UTII are applied at the same time, there are no employees, then the tax is also reduced.
- If the amount of the premium for insurance is greater than the amount of tax, then the excess finance is not transferred to another period.
- The right to tax reduction disappears when the entrepreneur recruits employees and gives them wages. If the individual entrepreneur stops paying employees, then the tax can only be reduced from the next period.
Reflection by postings
Medical insurance must be accompanied by postings:

Summing up, we can say that the purpose of health insurance is to guarantee that citizens receive first aid in case of a problem situation.
Citizens of the Russian Federation have equal rights and opportunities. You can contact the insurance organization yourself or through an intermediary (in this case, you will need a power of attorney).
Every resident of the Russian Federation must have an insurance policy, regardless of citizenship.It is issued free of charge; to obtain it, you need a document that certifies the person.