This contract is a type of property insurance contract, as indicated by paragraph 2 of part 2 of Art. 929 of the Civil Code, according to which a property interest such as the risk of liability under contracts can be insured under a property insurance contract (Article 932). In our case, such an agreement is a passenger carriage agreement.
There is no definition of a contract in the Law compulsory insurance civil liability carrier (hereinafter referred to as the compulsory insurance contract). But it indicates that this is an agreement in favor of a third party (beneficiary), which is concluded between the insurer and the policyholder in the manner and in the form established by the Civil Code for insurance contracts. The contract is a means of eliminating the consequences unfavorable for the carrier caused by its civil liability for damage during the transportation of the life, health, property of passengers.
Based on the specified purpose and belonging to the system of property insurance contracts, the compulsory civil liability insurance contract of the carrier can be defined as an agreement under which one party (the insurer) undertakes for the contractual fee (insurance premium) upon occurrence insured event(the occurrence of the carrier's obligations to compensate for damage during the transportation of life, health, property of passengers) to compensate the other party (the policyholder) or another person in favor of whom the contract was concluded (the beneficiary) for the caused losses within the amount specified in the contract.
The peculiarities of this contract are that, firstly, insurance of the risk of liability for violation of the contract for the carriage of a passenger in the form of harm to his life, health, property is directly provided for in paragraph 6 of Art. 3 of the Law, which corresponds to the provision of paragraph 1 of Art. 932 of the Civil Code, according to which insurance of the risk of liability for violation of the contract is allowed in cases stipulated by law. Therefore, this liability insurance contract cannot be regulated by another regulatory legal act. Secondly, the risk of liability of the insured himself and no other person is subject to insurance. Violation of this requirement means the nullity of the compulsory insurance contract (clause 2 of article 932 of the Civil Code).
This is a public contract. The insurer does not have the right to refuse its conclusion to any policyholder who has made such a proposal. In this case, the contract must be concluded on the same conditions for all.
It belongs to the number of real contracts. In accordance with part 2 of article 7 of the Law, the contract comes into force from the day the policyholder fulfills the obligation to pay the insurance premium or the first insurance premium.
This is a reciprocal and reimbursable contract.
Parties to the compulsory insurance contract- the insurer and the policyholder. Insurer under a compulsory insurance contract is insurance organization, which received a license to carry out compulsory insurance in accordance with the established procedure and entered into a single all-Russian professional association of insurers for the implementation of compulsory insurance (clause 8 of article 3 of the Law). An insurer that is not a member of a professional association of insurers is not entitled to carry out activities on compulsory insurance of the carrier's civil liability for damage to the life, health, property of passengers during transportation.
The Law regulates in sufficient detail the issues of the goals of the professional association of insurers, its status and powers. As a non-profit organization, a professional association of insurers operates in accordance with the provisions of the legislation on non-profit organizations provided for associations (unions). Among his powers should be highlighted such as the creation of a compensation fund, implementation compensation payments in accordance with the requirements of the Law, the formation and use of information resources containing information about compulsory insurance contracts, insured events, policyholders, victims, the amount of insurance payments and some others. The professional association of insurers ensures the exchange of information between its members, controls the timeliness and validity of insurance payments to victims. For this, it forms compensation fund at the expense of deductions from insurers.
Members of a professional association of insurers bear subsidiary responsibility for its obligations in terms of making compensation payments in proportion to the amount of funds allocated to finance these payments. one
In accordance with the Law, the members of the professional association of insurers form reinsurance pool for the reinsurance of the risks of civil liability of the carrier for causing harm to the life and health of the property of passengers. This is a union without education legal entity carries out joint activities of the specified subjects of reinsurance relations on the basis of a simple partnership agreement. Its purpose is to provide financial sustainability insurance operations for compulsory civil liability insurance of the carrier. It is achieved by distributing the risks accepted by this pool among the participants of the pool and establishing joint liability of the participants in the pool. The law contains a requirement according to which the participation of members of the professional association of insurers in the reinsurance pool is mandatory.
By the insured in the contract is the carrier carrying out the carriage of passengers who has entered into a compulsory insurance contract with the insurer (clause 9 of article 3 of the Law).
Among the participants in insurance relations, the Law on Compulsory Insurance of Civil Liability of the Carrier distinguishes the carrier himself. The legislative act defines the carrier and enshrines his duties and rights. It is a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur who is registered in the territory Russian Federation and in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, they carry out transportation regardless of the type of transport. 1 In fact, here, in general terms, the definition of a carrier given in transport charters and codes is reproduced, but an important point regarding the contractual nature of the carriage carried out by him is not noted. Meanwhile, it is this circumstance that indicates the fact that a legal entity or an individual entrepreneur acts as a carrier under the contract for the carriage of a passenger and, at the same time, as the policyholder is a party to the compulsory insurance contract.
It follows from the compulsory insurance contract that its participants include the beneficiary - the victim, whose health and (or) property is damaged. If harm is caused to the life of the victim, the beneficiaries in respect of reimbursement of the necessary expenses for the burial are the persons who actually incurred the costs. As for the rest of the insurance compensation, in relation to it - these are citizens who have the right to compensation for harm in the event of the death of the breadwinner in accordance with civil law, and in the absence of such citizens - the spouse, parents, children of the deceased, citizens with whom the victim was dependent, if he did not have an independent income.
Insurance object under the compulsory insurance contract, the property interests of the carrier are related to the risk of his civil liability for obligations arising from the infliction of harm to the life, health, property of passengers during transportation. The specified insured risk is limited to the sum insured. In accordance with the Law on Compulsory Insurance of Civil Liability of the Carrier (Article 8), in the compulsory insurance contract, the sums insured for each risk of civil liability must be indicated separately and amount to the following amounts, respectively:
- 1) at the risk of civil liability for causing harm to the life of the victim in the amount of at least two million twenty five thousand rubles;
- 2) on the risk of civil liability for causing harm to the health of the victim - in the amount of at least two million rubles per passenger;
- 3) at the risk of civil liability for causing damage to the property of the victim in the amount of at least twenty-three thousand rubles per passenger.
Compulsory insurance is a form of insurance in which an insurance relationship arises by virtue of the law. The initiator of compulsory insurance is the state, which in the form of a law obliges legal entities and individuals to contribute funds to ensure the public interest. The types, conditions and procedure for compulsory insurance are determined by the relevant laws of the Russian Federation.
Compulsory insurance means that insurance must be carried out by virtue of the state's command, regardless of whether the policyholder himself wants it or not.
Compulsory insurance is a form of insurance, the implementation of which is entrusted to the policyholder by law and is carried out through the conclusion of an insurance contract between the policyholder and the insurer. The policyholder carries out compulsory insurance at his own expense.
Compulsory insurance arises if one of the following conditions is met:
- voluntary insurance of such risks is commercially unprofitable for insurers;
- voluntary insurance is too expensive for the policyholder;
- the policyholder himself underestimates the severity of such risks.
But at the same time, there must be an objective social need for protection from such risks. In this case, the state adopts a law on compulsory insurance.
The initiative for the implementation of compulsory insurance belongs to the state, therefore such insurance always has a social connotation and expresses the concern of the state or about a certain layer of citizens (for example, insurance of passengers of air and railway transport where the risk of harm is greatest), or about certain property (for example, insurance of residential buildings owned by citizens, etc.). In other words, compulsory insurance means the establishment of insurance coverage for objects that are important for the whole society.
MANDATORY INSURANCE PRINCIPLES
There are the following principles of compulsory insurance:
1. The most important principle is the principle of obligation. Insurance is mandatory by virtue of the Law of the Russian Federation "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation".
2. An important principle of compulsory insurance is the principle of complete coverage. It lies in the fact that insurance companies, which are entrusted with compulsory insurance, must ensure 100% coverage of objects with this form of insurance, for which they must annually register objects subject to insurance.
3. Another important principle is the principle of automaticity, that is, the automatic nature of the distribution of compulsory insurance. Objects of compulsory insurance are included in the plans of insurance companies as the latter are registered, after which the policyholder automatically undertakes to increase insurance premiums under the terms and conditions established by law.
4. Another important principle of compulsory insurance is the principle of indefinite duration. It consists in the fact that the insurance is valid until the law (decree) on compulsory insurance is canceled or until the policyholder owns, uses and disposes of the insured property.
5. There is also the principle of the independence of making insurance payments. If the policyholder has not paid the premiums, then they are collected from him through the court. If at this time the property was damaged or lost, the insurer will pay insurance compensation, while withholding the debt (interest is charged on the debt).
6. The principle of rationing of insurance coverage. Compulsory insurance in its contract indicates the normalized amount of insurance coverage in the amount of a certain percentage of the property assessment. Or it can be a fixed amount, which is spelled out in insurance legislation for certain objects of insurance.
SIGNS OF OBLIGATORY INSURANCE
The signs of compulsory insurance can be divided into economic and legal.
The economic features of compulsory insurance include:
1. Mass character - involvement of a significant number of insured persons in insurance.
2. Universality - all persons falling under the category of the policyholder or the insured person must act in this capacity.
3. Comprehensiveness - all items subject to insurance must be insured.
4. Breadth of coverage - reaching a large number of insurance objects.
5. Affordability - an insurance infrastructure must be created that will allow the policyholder to carry out insurance without much hassle and difficulty.
6. Uniformity - the procedure and conditions of insurance are established by law, which ensures uniformity of insurance, regardless of who specifically acts as the policyholder and insurer and where this insurance is carried out.
7. Profitability - considering that persons who do not have significant incomes can be involved in insurance, the amount of insurance premiums is set as low as possible.
The legal features of compulsory insurance include:
1. Insurance is a government regulation.
2. Compulsory insurance is established by a legal act in the form of a federal law.
3. The conditions of insurance for the most part are determined by regulatory legal acts, and not by an agreement, as is typical of voluntary insurance.
4. Compulsory insurance is compulsory - the policyholder must carry out insurance regardless of whether he wants it or not.
5. Insurance is accompanied by the establishment of special protection of the interests of both the persons to be insured and persons who act as beneficiaries.
6. Evasion of policyholders from compulsory insurance entails established liability.
Compulsory insurance is carried out by concluding an insurance contract. An exception to this rule is compulsory state insurance, which can be carried out in a non-contractual form.
The insured under the compulsory insurance contract is the person who is entrusted with the obligation of such insurance.
TYPES OF OBLIGATORY INSURANCE
There are several types of compulsory insurance, each of which helps to organize a certain area of the social life of citizens:
- health insurance;
- social insurance;
- pension insurance;
- property insurance;
- motor third party liability insurance;
- insurance of liability for damage caused by the operation of a hazardous production facility;
- passenger insurance.
Health insurance- This is the most common type of compulsory insurance. OMS policy almost all residents of the country have, it provides broad guarantees in the provision of medical services.
The purpose of compulsory health insurance is to ensure the immediate provision of medical care at the expense of the fund's accumulative funds. Employers transfer money to the medical fund in the form of a deduction of 3.6% of the unified social tax.
To obtain a health insurance policy, you must contact the Territorial CHI Fund, the address of which can be found in the nearest clinic. When moving from one subject of the federation to another, you must hand over the old policy, and then get a new one.
However, you have the right to provide medical care anywhere in Russia, therefore, when leaving on a business trip or on vacation, be sure to take your policy with you.
Not all medical services are rendered free of charge, for example, preventive, sanitary-resort, cosmetology and other services carried out on the personal initiative of citizens are produced on a commercial basis.
To compulsory social insurance there are two types of insurance:
- social insurance in case of temporary disability and in connection with motherhood;
- social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases.
Mandatory pension insurance is developed by the state for the purpose of monetary compensation for the working population for retirement. The pension of every citizen of the Russian Federation is accumulated as a result of pension contributions. Due to insurance deductions from the place of work, accruals are created, which serve as an accumulation fund throughout the entire labor activity of the employee. At the same time, the amount of pension savings, regardless of deductions, can be independently increased. This becomes possible thanks to the voluntary investment of its own funded part in the Federal Pension Insurance Fund.
Each insured person is issued an insurance certificate of state pension insurance, which confirms the registration of the insured in the state pension insurance system of the Russian Federation.
Compulsory property insurance is the insurance of deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation, which is regulated by the Federal Law of December 23, 2003 No. 177-FZ "On insurance of deposits of individuals in banks of the Russian Federation". The objectives of the Law are to protect the rights and legitimate interests of depositors of banks in the Russian Federation, to strengthen confidence in the banking system of the Russian Federation and to stimulate the attraction of savings of the population to banking system RF.
OSAGO - compulsory motor third party liability insurance. All car owners know about this type of compulsory insurance. It guarantees compensation for harm to health, life or property in accident case... Motor third party liability insurance will not help in case of car theft or damage. For high payments and an extended insurance package, you will have to issue a CASCO, which is not cheap.
Compulsory civil liability insurance of the owner of a hazardous facility, which include:
- mines;
- mines;
- metallurgical plants;
- chemical shops;
- factories for the production of explosives;
- NUCLEAR POWER STATION;
- oil production platforms;
- warehouses for fuels and lubricants;
- flour mills;
- other enterprises with the possibility of a threat to life.
An ammonia leak, an explosion at a nuclear power plant, a collapse in a mine, a fire at a gas station - all these are accidents at hazardous facilities. In the event of an accident at a hazardous facility, all injured people receive insurance payments in an enlarged size.
Compulsory personal accident insurance for passengers applies to passengers of air, rail, sea, inland waterway and road transport, as well as tourists and excursionists making international excursions through tourist and excursion organizations, during a trip or flight. It is carried out through the conclusion of contracts between the relevant transport and transport-forwarding companies and insurers. This type of compulsory insurance does not apply to such a type of transport as a taxi.
Due to violations of the interests of citizens by carriers and the lack of guarantees of receiving payments, on January 1, 2013, OSGOP-Law No. 67 (Compulsory insurance of civil liability of carriers) came into force. The maximum payment is 2 million rubles, in the event of the death of a passenger, another 25 thousand rubles will be added to it for the funeral.
However, with the adoption of the law, the situation has changed little, since carriers in collusion with insurance companies in every possible way evade the fulfillment of their duties.
To receive payment in the event of an emergency, you will need to contact the insurer with a ticket and insurance receipt. Therefore, do not throw away your ticket and insurance until you arrive at your destination. The insurance is valid only for the duration of the trip.
A special type of compulsory insurance is compulsory state insurance. The subjects of this type of insurance include:
- military personnel;
- citizens called up for military training;
- persons of the rank and file and the commanding staff of the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation;
- employees of institutions and bodies of the penal system;
- employees of the federal tax police;
- employees, military personnel and employees of the State Fire Service.
The legislative framework
There are a number of legislative acts imputing compulsory state insurance for certain categories of persons. For example, these basic laws of the Russian Federation include:
Federal Law No. 3132-I Article 20 "On the Status of Judges in the Russian Federation", according to which the property, health and life of a judge is subject to compulsory state insurance for the total amount of wages over the past fifteen years.
Federal Law No. 45-FZ "On State Protection of Judges, Officials of Law Enforcement and Supervisory Bodies" states that other categories of persons are subject to compulsory insurance, such as: investigators, prosecutors, persons conducting inquests and others; Federal Law No. 3-FZ "On the status of a member of the Federation Council and the status of a deputy of the State Duma of the Federal Assembly of the Russian Federation".
Federal Law No. 5-FZ, Article 22 "On Foreign Intelligence", according to which the entire staff of foreign intelligence agencies is subject to insurance in the amount of one hundred and eighty official salaries (salaries); the insured is the foreign intelligence agency of the Russian Federation under the patronage of the President of the Russian Federation.
Federal Law No. 52-FZ “On Compulsory State Life and Health Insurance of Servicemen.
Federal Law N 403-FZ "On the Investigative Committee of the Russian Federation"
Other legislative acts.
Responsibility for violation of the rules on compulsory insurance
If it turns out that compulsory insurance has not been carried out, then the person in whose favor it should have been made has the right to judicially demand from the person who is entrusted with the obligation to insure its implementation.
In case of non-implementation of compulsory insurance by the person who is charged with the insurance obligation or if an insurance contract is concluded, but its conditions violate the interests of the beneficiary, then in the event of an insured event, the person is liable to the beneficiary in the amounts that would have been established with proper insurance.
The amounts saved by a person with inadequate insurance are recovered to the state income with interest accrued in accordance with Art. 395 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation.
1. A compulsory insurance contract is concluded in relation to each hazardous facility, unless otherwise provided by the contract in relation to hazardous facilities specified in Clause 4 of Part 1 of Article 5 of this Federal Law, for a period of at least one year. The document confirming the conclusion of a compulsory insurance contract is an insurance policy of the established form, which is handed over by the insurer to the policyholder after he has paid the insurance premium or the first insurance premium.
(see text in previous edition)
2. The compulsory insurance contract is a public contract.
3. The compulsory insurance contract enters into force from the day the policyholder fulfills the obligation to pay the insurance premium or the first insurance premium or from another day specified in the compulsory insurance contract, provided that insurance premium or the first insurance premium was paid before the date of entry into force of the compulsory insurance contract.
4. When the owner of a hazardous facility changes during the period of validity of the compulsory insurance contract, the rights and obligations of the policyholder under this contract are transferred to the new owner of the hazardous facility, if the new owner of the hazardous facility within 30 calendar days from the date of taking possession of the hazardous facility in writing insurer. In the absence of such notification, the compulsory insurance contract terminates from 24 hours local time on the last day of the specified thirty-day period, and the policyholder with whom the compulsory insurance contract was originally concluded has the right to demand the return of part of the insurance premium paid by him in proportion to the unexpired insurance period minus the costs incurred by the insurer for maintaining cases and deductions to the reserve for financing compensation payments.
5. In the event that a hazardous facility has ceased to comply with the requirements established by this Federal Law for dangerous facilities the owners of which are obliged to carry out compulsory insurance, the policyholder has the right to early terminate the compulsory insurance contract and demand the return of a part of the insurance premium paid by him in proportion to the unexpired period of insurance minus the costs incurred by the insurer for the conduct of the case and deductions to the reserve for financing compensation payments.
6. Upon termination of the compulsory insurance contract, the insurer, at the request of the policyholder, provides him with information on the number and nature of the insured events that have occurred, on the insurance payments made and on the upcoming, considered and unsettled claims of the victims on insurance payments during the period of the specified contract (hereinafter - information on compulsory insurance ). Information on compulsory insurance is provided by the insurer in writing and free of charge.
Content
Life often brings unpleasant surprises in the form of fires, car accidents, illness, or layoffs. To protect against such troubles, you must follow the safety rules. But if this happens, the only financial aid is the insurance service against all these risks. To do this, it is necessary to conclude an insurance contract, which must be drawn up in accordance with all the rules of law in accordance with the civil code of the Russian Federation.
What is an insurance contract
According to the civil legislation of the Russian Federation, a distinction is made between voluntary and compulsory insurance. In the first case, the client himself decides to insure himself or his property against certain risks. For insurance, it is necessary to conclude a direct agreement between the person who wishes to be insured and the insurer who has the right to do so under a license or power of attorney.
Private
When insuring against the risks of loss of life, deterioration of health, loss of work, the policyholder is required to conclude a personal insurance contract. According to civil law, this type of insurance is completely voluntary. It is allowed with the consent of the insured to conclude an agreement on the terms of the insurance company (IC). The obligation of the IC is to pay the policyholder upon the occurrence of an insured event the amount of insurance specified in the policy.
Property
Property insurance is used to reduce the risks of loss or damage to property and commercial cargo. According to the Law of the Russian Federation "On the organization of insurance business in the Russian Federation" property interests are the object of insurance. For loans secured by collateral or mortgages, the borrower insures the purchased property at his own expense, for car loans - a car. In the event of an insured event, the insurer is obliged to compensate for the damage within the agreed amount to the owner. In the policy, it is possible to replace the policyholder.
Kinds
There are three main types of policies, differing in objects of insurance and types of insured event:
- personal - the IC undertakes, in the event of harm to life and health or the occurrence of the specified event, to pay the insured amount to the insured person or another person;
- property (general or ordinary) - the policyholder or the beneficiary is compensated for damage in case of damage or destruction of the insured object in accordance with the amount of losses;
- liability risk insurance - the risk of liability is insured for causing damage, harm to third parties by the policyholder himself or by another person on whom such liability may be assigned;
- reinsurance - protection of the risks of the IC itself.
By legal nature
From the moment the insurance premium is paid, the agreements are valid. They are concluded by mutual agreement of the insurer and the policyholder, and are consensual. The insurance contract is urgent, reimbursable, public and risky. According to the correspondence of the basis of the obligation to the nature of the insurance legal relations themselves, it belongs to the group of casual transactions. One of the main conditions of these legal relations is their obligation and observance of a compensatory nature.
Depending on the object of insurance
The main difference between agreements and insurance principles is the choice of the object. In this case, two options are possible - personal and property insurance. In his personal form, everything that is associated with a specific person is insured - his life, health, job loss and others. Property insurance protects the risks of partial or complete loss of the insured property as a result of specific types of impacts - fire, flooding, floods, accidents. In the event of the events specified in the insurance policy, the victim will receive compensation in the specified amount.
Form
The insurance contract provides for a written form. Failure to comply with the written form entails its invalidity, with the exception of the policy of compulsory state insurance. The insurer has the right to apply the developed standard forms of the policy for the types of insurance. The insurance contract can be concluded by drawing up one written document or by handing it over by the insurer on the basis of the policyholder's application signed by the insurer.
Mandatory
The Civil Code establishes the following types of compulsory insurance:
- insurance in case of damage to property or harm to health in the performance of their duty;
- civil liability risk insurance, which can be used to compensate for harm to life, health or compensation for damage to property of third parties;
- insurance of property that is state or municipal property and that belongs to legal entities.
Voluntary
Modern Insurance companies offer protection against various risks. They can be divided into the following types of insurance:
- life - in the event of the death of the insured person, a certain amount is paid to relatives or other specified persons;
- pension insurance - in which a citizen independently forms his own pension savings fund;
- from accidents - protection from injury, illness or disability;
- housing - insurance of apartments, houses, summer cottages;
- animals - compensates the owner for the costs arising from illness or injury of the animal, applies to farm animals.

Mandatory state
In accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation (Article 969), state organizations (institutions) are health and life insurers for a certain category of persons, provided with guarantees and mandatory health insurance due to the operation of special laws, these include:
- military personnel;
- citizens called up for military training;
- persons of the rank and file of the internal affairs bodies of the Russian Federation;
- employees of institutions and bodies of the UIN system;
- federal tax police officers;
- employees, military personnel and employees of the State Fire Service.
Subject and subjects
The main actors and the subject of the insurance contract:
- insurer - a legal entity licensed by the Insurance Supervision Department of the Ministry of Finance of Russia;
- insured - a natural or legal person who has entered into an agreement with the insurer;
- beneficiary (beneficiary) - a person in whose favor the policy was concluded;
- insured person - an individual in whose favor the policies have been issued;
- term - from the date of payment of the premium, contribution or other conditions until the date of completion or early termination of the contract.
Essential conditions
When concluding a policy, an agreement must be reached between the parties, including the essential terms of the insurance contract. Legal conditions without which the policies are invalidated are recognized as material:
- About the subject of the policy or the object of insurance - certain property or risks of loss, shortage or damage to property, risks of civil liability, business risks.
- About the insured event - it is determined which moments will be considered as such and upon the occurrence of which the sum insured is payable.
- What is the amount of the sum insured, the procedure for payment.
- On the amount of the franchise - the part of the property value that is not subject to insurance compensation upon the occurrence of an insured event. The conditions or shares of insurance companies may apply zero deductibles for certain types of accidents - breaking glass or headlights of cars, destruction of the roof, etc.
- About the validity period of the policy.
The personal insurance policy must necessarily take into account:
- the presence of an insured person;
- a list of events, the occurrence of which will be considered an insured event;
- the amount and procedure for payment of the insured amount;
- validity.

Poor conditions
Illegal conditions that entail the invalidity of contracts may be insurance:
- if the sum insured is greater than the value of the insured object;
- losses from participation in games, lotteries, bets;
- expenses that a person may be forced to incur in order to free the hostages;
- illegal interests.
When comes into force
As a general rule, the insurance premium must be paid for the contract to enter into force. By agreement between the parties, this may be the moment of its signing. The policy may provide for the possibility of paying the premium in installments - then the policy comes into force from the moment the first installment is paid. All these cases must be clearly stated in the policy.
Rights and obligations of the parties
Policyholder's rights:
- upon the occurrence of an insured event provided for by the policy, payment is received in accordance with its terms;
- replacement of the beneficiary by written consent of the policyholder;
- demand from the insurer the proper performance of obligations without violations;
- for early termination of the contract;
- upon the death of the insured person, his heirs are recognized as beneficiaries.
The insurer has the right:
- demand payment of contributions, receive a bonus in the amount and in the manner provided for in the agreement;
- conduct a risk assessment and, on the basis of this, invalidate agreements.
- develop and implement additional rules insurance;
- submit recourse claims;
- if the risk increases, demand a change in the terms of the contract and an increase in the premium.
Insurer and policyholder
Obligations of the policyholder:
- pay the insurance premium on the terms specified in the policy;
- if there is a likelihood of the occurrence of an insurance event, he is obliged to notify the insurer;
- notify the insurer about the occurrence of an insured event;
- ensure that the necessary measures are taken to reduce losses from the insured event.
Obligations of the insurer:
- the insurer has the main obligation to pay the amount of insurance upon the occurrence of an insured event at a written application and request of the policyholder.

Consequences of non-fulfillment of obligations
When deliberately giving false information when concluding a contract, the insurer has the right to demand that the policy be declared invalid. During its validity, the policyholder is obliged to inform the insurer of all changes in the circumstances reported upon its conclusion. If the policyholder "forgets" to notify the insurer about the occurrence of the insured event, the insurer has the right to refuse to pay compensation. If the policyholder deliberately does not take measures to reduce losses in the event of an insured event, and this is proven in court, the insurer is exempted from damages.
Conclusion procedure
Article 940 of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation provides for a mandatory written form of contracts. Failure to comply with this condition entails its complete invalidity. The conclusion of the contract is made by drawing up one document or by handing over the policy to the policyholder. The agreement is considered concluded from the moment it is signed by the policyholder. Insurance policy - a personalized document confirming the fact of insurance. Issued to the policyholder after signing the agreement and paying the premium.
The insurance policy must contain:
- indication and characteristics of the object;
- the amount of the insured amount;
- indication of risk;
- amount of the contribution, terms, payment procedure;
- validity period, procedure for change, termination;
- other conditions by agreement of the parties, additions, exceptions;
- name, legal address and bank details of the insurer and the policyholder;
- signatures of the parties.
What is the sum insured
Sum insured- the amount determined by the agreement or established by law, within which the insurer undertakes to pay the insurance indemnity upon the occurrence of an insured event. The sum insured is the maximum amount of the insurer's liabilities for insurance payments. Based on the sum insured, the amount of insurance premiums and payments is established. The insured amount stipulated by the contract may not exceed the insured value of the property.
Insurance premium
This is the amount of money that the policyholder is obliged to pay to the insurer in accordance with the policy. The insurance premium paid by the policyholder to the insurer in accordance with the policy or law. In case of early refusal of the policyholder from the insurance policy, the insurance premium paid to the insurer shall not be refunded, unless otherwise provided by the policy.

Termination
The insurance contract is terminated in the following cases:
- expiration date;
- fulfillment by the insurer of obligations in full;
- failure to pay insurance premiums by the insured within the established time frame;
- liquidation of the policyholder or insurer;
- a court decision to invalidate the policy.
In what cases the contract is considered invalid
To confirm the invalidity of the policy, an application must be submitted with an indication of compelling reasons for its termination to the arbitration court. All stages of the trial will be required, for which the facts of violations are necessary. After a court investigation, the policy is invalidated by a court decision. The insurance contract is considered invalid if:
- it is concluded after the occurrence of the insured event;
- the object of insurance is non-insurance events;
- this type of insurance is not provided for by the IC license;
- insurance activities are carried out outside the territory specified in the license.
Limitation of actions
By the Resolution of the Plenum of the Supreme Court of the Russian Federation of September 29, 2015 No. 43 "On some issues related to the application of the rules of the Civil Code of the Russian Federation on statute of limitations", the statute of limitations for property insurance is two years. The limitation period for obligations arising from harm to the life, health or property of others is three years.
Video
Found a mistake in the text? Select it, press Ctrl + Enter and we'll fix it!DEPARTMENT OF STATE ORDER
TOMSK REGION
On the approval of a standard contract for the provision of services
by compulsory
________________________________________________________
Abolished from 01.03.2018 on the basis of
Order of the Department of State Order of the Tomsk Region dated February 26, 2018 No. 2-p
_______________________________________________________________
In accordance with part 7 of article 112 of the Federal Law of April 5, 2013 No. 44-FZ "On the contract system in the field of procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs"
I order:
1. To approve the model contract of insurance of civil liability of owners Vehicle(OSAGO) in accordance with the appendix to this order.
2. This order comes into force on September 1, 2017.
3. I reserve control over the execution of this order.
Head of department
G.V. Gongina
Model contract for the provision of services for compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners (OSAGO)
Appendix
APPROVED BY
by order of the Department
state
order of the Tomsk region
dated 09/08/2017 No. 12-p
Project
STATE CONTRACT (CONTRACT) No. ____
for the provision of services for compulsory civil liability insurance
vehicle owners (OSAGO)
Tomsk (1) "____" ___________ 20__
_________________________
(1) May be changed as required.
On behalf of the Tomsk region (2), representing ___ ["Government Customer" ("Customer")](3), we refer to ___ hereinafter as the "Policyholder", represented by __________________, acting on ___ on the basis of __________, on the one hand, and ______________, being ___ "Contractor", we refer to ___ hereinafter as the "Insurer", represented by ______________________________, acting on ___ on the basis of __________, on the other the parties, collectively referred to as the "Parties" and each individually "Party", on the basis of the protocol ___________________ No. __________ dated "____" _________ 201__ (4), have concluded this [State contract, hereinafter referred to as the Contract, (Contract)](5) about the following:
_________________________
(2) Specified if necessary. (3) Selected in accordance with the concepts specified in Article 3 of the Federal Law of April 5, 2013 No. 44-FZ "On the contract system in the procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs" (hereinafter - Law No. 44-FZ.) (4) The protocol is indicated, according to which the Contractor was determined, with whom the contract is concluded. (5) It is selected in accordance with article 3 of Law No. 44-FZ.
1. Object of the procurement (subject of the contract)
1.1. The Insurer undertakes to provide the Insured with services for compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners specified in Appendix 1 to the Contract, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners, and the Policyholder shall pay and accept services in the manner and on the conditions provided for in Contract.
Purchase identification code: ____________________________.
2. Contract price and payment procedure
2.1. The Contract price consists of [insurance premium for a vehicle (from the amounts of insurance premiums for each vehicle)](6) indicated (s) in Appendix 1 to the Contract, and amounts to _______ (________) rubles ___ kopecks, value added tax is not levied on the basis of subparagraph 7 of paragraph 3 of Article 149 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation.
_________________________
(6) The desired option is indicated.
The contract price includes all costs associated with the provision of services in accordance with the terms of the Contract, including:
- the cost of providing services;
- the cost of paying taxes, fees and other mandatory payments;
- all unforeseen expenses that may arise during the period of the Contract in connection with its execution.
Insurance (s) the prize (-and) calculated (s) The insurer as the product of base rates and coefficients of insurance rates in accordance with the procedure for the application of insurance rates for compulsory insurance by insurers when determining the insurance premium under a compulsory insurance contract established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in accordance with Article 8 of Federal Law No. 40-FZ dated April 25, 2002 "On compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners."
A change in insurance rates does not entail a change in the insurance premium paid by the Insured according to the insurance rates in force at the time of payment under the Contract during its validity period.
The maximum value of the contract price set in the procurement documentation is calculated using the price formula in accordance with Appendix 2 to the Contract and is _______ (________) rubles ___ kopecks.
2.2. Insurance payment (s) prizes (th) is made by the Insured at a time by transferring Money to the current account of the Insurer specified in the Contract on the basis of the invoice submitted by the Insurer within ______ working days (-his) days (-I am) after receiving it.
Insurance invoice (s) prizes (th) issued by the Insurer to the Policyholder within
(7) working them (s) day her (s) from the date of receipt of the documents specified in Art. (eight)
_________________________
(7) Condition may be changed if necessary. (8) Clause may be changed if necessary.
2.3. On the day the Insured fulfills the obligation to pay for the insurance (s) prizes (th) the day the funds are debited from the personal account of the Insured is considered.
2.4. The collection of all documents necessary for payment is carried out by the Insurer.
2.5. The currency used for settlements is the Russian ruble.
2.6. Source of financing: _________________________ .
3. Rights and obligations of the parties
3.1. The policyholder has the right:
3.1.1. Demand from the Insurer the proper performance of obligations in accordance with the terms of the Contract.
3.1.2. Require the Insurer to submit properly executed documents.
3.1.3. Request information from the Insurer on the progress and status of fulfillment of the Insurer's obligations under the Contract.
3.1.4. Submit a motivated refusal to sign the acceptance certificate for the services rendered [other documents ______] based on the results of acceptance of the services rendered.
3.1.5. Use other rights established by the Contract and the legislation of the Russian Federation.
3.2. The policyholder is obliged:
3.2.1. Submit to the Insurer the documents specified in Article 15 of the Federal Law of April 25, 2002 No. 40-FZ "On Compulsory Insurance of Civil Liability of Vehicle Owners".
3.2.2. Pay on the basis of the Insurer's invoice for the insurance (s) the prize (-and).
3.2.3. Accept the services rendered in the absence of comments on the quality, volume, compliance of the services rendered with the terms of the Contract.
3.2.4. Before collecting a forfeit (fines, penalties), observe the claim procedure for resolving a dispute (send the Insurer a claim containing a requirement to pay the amounts of the forfeit (fines, penalties) provided for by the Contract for non-performance (improper performance) by the Insurer of its obligations under the Contract).
3.2.5. Perform other obligations stipulated by the Contract and the legislation of the Russian Federation.
3.3. The insurer has the right:
3.3.1. Require payment of insurance (s) prizes (th).
3.3.2. Request the Policyholder to provide clarifications and clarifications on the provision of services under the Contract.
3.3.3. Require the Insured to fulfill the obligations stipulated by the Contract and the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
3.3.4. Use other rights established by the Contract and the legislation of the Russian Federation.
3.4. The insurer is obliged:
3.4.1. Issue insurance to the Policyholder (s) policy (s) immediately after the policyholder fulfills the obligation to pay the insurance (s) prizes (th).
Transfer of insurance (s) policy (s) carried out in the following way: _________. (9)
_________________________
(9) Clause can be changed if necessary.
3.4.2. Not provide other persons or otherwise disclose confidential information obtained as a result of the fulfillment of obligations under the Contract.
3.4.3. At the request of the Policyholder, provide reliable information on the progress of the fulfillment of their obligations, including on the difficulties arising in the performance of the Contract in the manner specified in clauses 11.7, 11.8 of the Contract.
3.4.4. Prior to collecting a forfeit (fines, penalties), observe the claim procedure for resolving a dispute (send the Insured a claim containing a requirement to pay the amounts of the forfeit (fines, penalties) provided for by the Contract for non-performance (improper performance) by the Insured of its obligations under the Contract).
3.4.5. Perform other obligations stipulated by the current legislation of the Russian Federation and the Contract.
4. Place and terms of rendering services, quality of services
4.1. Place of provision of services: _______________.
4.2. Terms of services rendering: _______________.
4.3. The provision of services for compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners is carried out by the Insurer in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners.
5. Procedure for accepting services rendered
5.1. The policyholder accepts the services provided within
(10) working them (s) day her (s) [from the date of receipt insurance policy(last insurance policy)] (11).
_________________________
(10) The condition can be changed if necessary. (11) The required option is indicated, the condition can be changed if necessary.
5.2. The insurer no later than
(12) working their (s) of the day (day, days), must notify the Insured in writing about the readiness of services for delivery. Notice must also be sent by e-mail: _________________ or fax: _____________.
_________________________
(12) The condition can be changed if necessary.
5.3. To check the services provided in terms of compliance with the terms of the Contract, the Insured conducts an examination. The examination is carried out by the Insured on its own or with the involvement of experts, expert organizations.
To conduct an examination of the services provided, experts, expert organizations have the right to request from the Insurer additional materials related to the terms of the Contract execution. The term for the submission of additional materials by the Insurer is
(13) working their (s) of the day (day, days) from the moment of sending the request. If the Insurer violates the deadline for submission of additional materials, the deadline for acceptance of the services provided, provided for in clause 5.1 of the Contract, increases by the number of days of delay. (14)
_________________________
(13) The condition may be changed if necessary. (14) This paragraph may be changed if necessary, in accordance with the requirements provided for in Articles 94 and 95 of Law No. 44-FZ.
5.4. In case of detection of deficiencies (in terms of volume, quality, other deficiencies), the Policyholder notifies the Insurer no later than
(15) working them (s) day her (s) from the date of discovery of the indicated deficiencies. A notice of the identified deficiencies with an indication of the time frame for eliminating the deficiencies is sent to the Insurer by telegram, mail, e-mail, fax or courier. The email address for sending notices is: ______________. The fax number for sending notifications is: ________________.
_________________________
(15) The condition can be changed if necessary.
5.5. Upon completion of acceptance of services, the Policyholder within
(16) working them (s) day her (s) signs the acceptance certificate of the services rendered [other documents _______] or sends a reasoned refusal to sign the acceptance certificate for the services rendered [other documents _______]... In case of non-compliance of the services with the terms of the Contract, the acceptance certificate of the services rendered [other documents __________] not signed until the deficiencies are eliminated by the Insurer.
_________________________
(16) The condition can be changed if necessary.
5.6. The date of performance by the Insurer of the obligations provided for in clause 1.1 of the Contract is the date of signing by the Insured of the acceptance certificate of the services rendered. [other documents _____] without comments .
6. Responsibilities of the parties
6.1. The parties are responsible for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment of obligations in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
6.2. Losses incurred as a result of non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment by the Parties of obligations under the Contract shall be reimbursed in the amount and in the manner prescribed by the legislation of the Russian Federation.
6.3. In case of delay in the performance of the Policyholder's obligations under the Contract, as well as in other cases of non-performance or improper performance by the Policyholder of the obligations under the Contract, the Insurer has the right to demand payment of penalties (fines, penalties).
Penalty is charged for each day of delay in the fulfillment of the obligation provided for by the Contract, starting from the day following the day of expiry of the term for the fulfillment of such an obligation established by the Contract in the amount of one three hundred of the refinancing rate effective on the date of payment of the penalty interest The central bank Of the Russian Federation from the amount unpaid on time.
Penalties are charged for improper fulfillment by the Insured of the obligations stipulated by the Contract, with the exception of the delay in the fulfillment of the obligations stipulated by the Contract. The amount of the fine is _________ percent s (s) of the Contract price (2.5 percent of the Contract price if the Contract price does not exceed 3 million rubles; 2 percent of the Contract price if the Contract price is from 3 million rubles to 50 million rubles; 1.5 percent of the Contract price if the Contract price is from 50 million rubles to 100 million rubles; 0.5 percent of the Contract price if the price of the Contract exceeds 100 million rubles), _______ (________) rubles ___ kopecks. (17)
_________________________
(17) The amount of the fine is set in the form of a fixed amount determined in the manner prescribed by the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 25, 2013 No. 1063 "On approval of the Rules for determining the amount of the fine charged in the event of improper performance by the customer, supplier (contractor, performer) of the obligations provided for the contract (except for the delay in the fulfillment of obligations by the customer, supplier (contractor, performer), and the amount of the penalty charged for each day of delay in the performance by the supplier (contractor, performer) of the obligation stipulated by the contract. "
6.4. In case of delay in performance by the Insurer of the obligations stipulated by the Contract, as well as in other cases of non-performance or improper performance by the Insurer of the obligations under the Contract, the Policyholder sends the Insurer a claim containing a claim for payment of penalties (fines, penalties).
Penalty is charged for each day of delay in the performance of the obligation by the Insurer, starting from the day following the day of expiry of the deadline for the performance of the obligation established by the Contract until the day of actual performance of the obligation (inclusive), and is established by the Contract in the amount determined in the manner established by the decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of November 25, 2013 No. 1063 "On approval of the Rules for determining the amount of the fine charged in the event of improper performance by the customer, supplier (contractor, performer) of the obligations stipulated by the contract (except for the delay in performance of obligations by the customer, supplier (contractor, performer), and the amount of interest charged for each day) delay in the fulfillment by the supplier (contractor, performer) of the obligation stipulated by the contract ", but not less than one three hundredth of the refinancing rate of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation in effect on the date of payment of the penalty interest from the price of the Contract, reduced by an amount proportional to the amount of obligations stipulated by the Contract and actually fulfilled by the Insurer, and is determined by the formula:
(where C is the price of the contract; B is the cost of the contractual obligation actually fulfilled by the Insurer on time, determined on the basis of the document on the acceptance of goods, the results of work, the provision of services, including individual stages of the execution of contracts; C is the rate).
The size of the bet is determined by the formula:
(where Csb is the size of the refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of payment of the penalty, determined taking into account the coefficient K; DP is the number of days of delay).
The coefficient K is determined by the formula:
(where DP is the number of days of delay; DC is the deadline for fulfilling the obligation under the contract (number of days).
With K equal to 0 - 50 percent, the rate is determined for each day of delay and is taken to be equal to 0.01 of the refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of payment of the penalty.
With K equal to 50 - 100 percent, the rate is determined for each day of delay and is taken equal to 0.02 of the refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of payment of the penalty.
If K is equal to 100 percent or more, the rate is determined for each day of delay and is taken equal to 0.03 of the refinancing rate established by the Central Bank of the Russian Federation on the date of payment of the penalty.
Penalties are charged for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment by the Insurer of obligations, with the exception of delay in fulfillment by the Insurer of the obligations stipulated by the Contract. The amount of the fine is _________ percent (-ov, -a) of the Contract price (10 percent of the Contract price if the Contract price does not exceed 3 million rubles; 5 percent of the Contract price if the Contract price is from 3 million rubles to 50 million rubles; 1 percent of the Contract price if the price of the Contract is from 50 million rubles to 100 million rubles; 0.5 percent of the price of the Contract if the price of the Contract exceeds 100 million rubles), _______ (________) rubles ___ kopecks. (eighteen)
_________________________
(18) The amount of the fine is set in the form of a fixed amount determined in the manner prescribed by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation dated November 25, 2013 No. 1063 "On approval of the Rules for determining the amount of the fine charged in the event of improper performance by the customer, supplier (contractor, performer) of the obligations provided for the contract (except for the delay in the fulfillment of obligations by the customer, supplier (contractor, performer), and the amount of the penalty charged for each day of delay in the performance by the supplier (contractor, performer) of the obligation stipulated by the contract. "
6.5. A Party is exempted from paying a forfeit (fine, penalty) if it proves that the failure to fulfill or improper fulfillment of the obligation provided for in the Contract was due to force majeure or through the fault of the other Party.
6.6. Payment of penalties (fines, penalties) and compensation for losses caused by improper performance of obligations does not relieve the Parties from fulfilling their obligations under the Contract in full.
6.7. Payment of penalties (fines, penalties) is carried out on the basis of a written claim of one of the Parties.
6.8. The Policyholder has the right to take into account when settling with the Insurer (deduct from the price of the Contract) the amount in the form of a forfeit (fine, penalty) payable by the Insurer for non-performance (improper performance) of the obligations stipulated by the Contract, unless the Insurer proves that failure (improper performance) of obligations has occurred due to force majeure or the fault of the other Party.
7. Procedure for resolving disputes
7.1. All disputes or disagreements arising between the Parties under the Contract or in connection with it shall be resolved through negotiations in a complaint procedure. The term for consideration of the claim is
(19) working their (s) days (day, day) from the date of its receipt, except for cases for which the legislation of the Russian Federation on compulsory insurance of civil liability of vehicle owners provides for other terms for considering a claim.
_________________________
(19) The condition can be changed if necessary.
7.2. If it is impossible to resolve disagreements through negotiations in a complaint procedure, they are subject to consideration in the Arbitration Court of the Tomsk Region.
8. Procedure for changing, supplementing and terminating the contract
8.1. By agreement of the Parties, the volume of services provided for by the Contract may be increased by no more than ten percent, or the volume of services provided for by the Contract can be reduced by no more than ten percent.
At the same time, by agreement of the Parties, it is allowed to change, taking into account the provisions of the budgetary legislation of the Russian Federation, the price of the Contract in proportion to the additional volume of services, based on the price of a unit of service established in the Contract, but not more than ten percent of the price of the Contract. In the event of a decrease in the scope of services provided for by the Contract, the Parties to the Contract are obliged to reduce the price of the Contract based on the price of a unit of service. (twenty)
_________________________
(20) This clause is included in the draft Contract if there are grounds provided for in subclause b of clause 1 of part 1 of Article 95 of Law No. 44-FZ. In this case, the Contract must necessarily indicate the price per unit of service.
8.2. Termination of the Contract is allowed by agreement of the Parties, by court decision [
, as well as in case of unilateral refusal by the Party to execute the Contract in accordance with civil law] (21).
_________________________
(21) The condition on the possibility of unilateral refusal to perform the Contract is included in the clause if necessary.
8.3. The Policyholder decides to unilaterally refuse to execute the Contract in the cases specified in Part 15 of Article 95 of the Federal Law of April 5, 2013 No. 44-FZ "On the contract system in the field of procurement of goods, works, services to meet state and municipal needs."
9. Force majeure circumstances
9.1. The circumstances, the occurrence of which exempts from liability for violation of the obligation, are force majeure circumstances, such as: armed conflicts, acts of terrorism, legal acts of state bodies, emergency and other emergencies, strikes, riots, if such circumstances directly affect the ability of the Party to fulfill corresponding commitment.
9.2. In case of non-fulfillment or partial failure of any of the Parties to fulfill the obligations under the Contract due to the occurrence of the circumstances specified in clause 9.1 of the Contract, if they directly influenced the timing of the fulfillment by the Parties of their obligations, the deadline for the fulfillment of obligations is postponed in proportion to the time during which these circumstances will operate.
9.3. The Party, for which the impossibility of fulfilling obligations due to the above reasons has been created, must notify the other Party in writing within 5 (five) working days from the date of such circumstances. The proof of the facts specified in the notification must be the documents issued by the competent authorities.
9.4. Failure to notify or untimely notification of the other party in accordance with clause 9.3 of the Contract entails the loss of the right to refer to these circumstances.
10.Ensuring the performance of the contract
10. ENSURING THE PERFORMANCE OF THE CONTRACT(22)
_________________________
(22) This section included in the draft Contract in the cases specified in Article 96 of Law No. 44-FZ.
10.1. The amount of the security for the performance of the Contract is _______ percent s (s) the initial (maximum) price of the Contract in the amount of __________ (________) rubles. (23)
_________________________
(23) If there are grounds provided for in Article 37 of Law No. 44-FZ, the amount of the security for the performance of the Contract is changed in accordance with this Article.
10.2. The security for the performance of the Contract is provided by the Insurer in the following way: [irrevocable bank guarantee issued by the bank (deposit of funds to the account of the Insured, on which, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, transactions with funds received by the Insured are taken into account)] (24).
_________________________
(24) The desired option is indicated.
10.3. The document confirming the provision of security for the performance of the Contract is an integral part of the Contract.
10.4. Funds from the security for the performance of the Contract are payable to the Insured as compensation for non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment by the Insurer of its obligations under the Contract, including the payment of forfeit (penalties, fines), to reimburse any losses to the Insured caused by non-fulfillment or improper fulfillment by the Insurer of its obligations under the Contract , as well as for the return of the insurance premium.
10.5. If the Insurer determines the method of ensuring the execution of the Contract "Depositing funds to the account of the Insured, where, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, transactions with funds received by the Insured are accounted for", the security for the execution of the Contract is returned by the Insured to the Insurer within
(25) working them (s) day her (s) from the date of signing by the Parties of the acceptance certificate of the services rendered [the last act of acceptance of the services rendered] [other documents _____] on the basis of a written request from the Insurer.
_________________________
(25) The condition can be changed if necessary.
10.6. If, for any reason, the security for the fulfillment of obligations under the Contract has ceased to be valid, has expired or otherwise ceased to ensure the fulfillment by the Insurer of its obligations under the Contract, the Insurer undertakes to provide the Insured with new proper security for the fulfillment of obligations within 5 (five) business days under the Contract on the terms and in the amount specified in this section.
10.7. The Insurer has the right to provide the Policyholder with security for the performance of the Contract, reduced by the amount of fulfilled obligations stipulated by the Contract, instead of the previously provided security for the performance of the Contract. In this case, the method of ensuring the execution of the Contract may be changed.
10.8. If the Insurer determines the method of ensuring the execution of the Contract "Irrevocable bank guarantee issued by the bank", the validity period of the bank guarantee must exceed the validity period of the Contract by at least one month.
10.9. Settlements are accompanied by ______________________ (26) and is reflected in the accounts that are opened with the specified bank. (27)
_________________________
(26) The name of the bank shall be indicated. (27) This clause shall be included in the draft Contract in the event that a condition for banking support of the Contract is established (Article 35 of Law No. 44-FZ).
11. Other conditions
11.1. The object of compulsory insurance is property interests associated with the risk of civil liability of the owner of the vehicle (the Insured) for obligations arising from harm to the life, health or property of the victims when using the vehicle on the territory of the Russian Federation.
11.2. An insured event is the occurrence of civil liability of the owner of the vehicle (the Insured) for causing harm to the life, health or property of the victims when using the vehicle, entailing, in accordance with the Contract, the obligation of the Insurer to make insurance indemnity.
11.3. The insurance risk for compulsory insurance includes the occurrence of civil liability for the obligations specified in clause 11.1 of the Contract, except for cases of liability arising due to:
a) causing harm when using a vehicle other than that specified in Appendix 1 to the Contract;
b) infliction of moral harm or the emergence of an obligation to compensate for lost profits;
c) causing harm when using vehicles during competitions, tests or training driving in specially designated places;
d) environmental pollution;
e) damage caused by the impact of the transported cargo, if the risk of such liability is subject to compulsory insurance in accordance with the law on the corresponding type of compulsory insurance;
f) causing harm to the life or health of employees in the performance of their labor duties, if this harm is subject to compensation in accordance with the law on the appropriate type of compulsory insurance or compulsory social insurance;
g) obligations to reimburse the employer for losses caused by causing harm to the employee;
h) causing damage by the driver to the vehicle he is driving and the trailer to it, the cargo carried by them, the equipment installed on them and other property;
i) causing harm when loading cargo onto a vehicle or unloading it;
j) damage or destruction of antiques and other unique items, buildings and structures of historical and cultural significance, items made of precious metals and precious and semiprecious stones, cash, valuable papers, items of a religious nature, as well as works of science, literature and art, other objects of intellectual property;
k) causing harm to the life, health, property of passengers during their transportation, if this harm is subject to compensation in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation on compulsory insurance of the carrier's civil liability for harm to the life, health, property of passengers.
11.4. The sum insured, within which the Insurer, upon the occurrence of each insured event (regardless of their number during the term of the Contract), undertakes to compensate the injured for the damage caused, is:
a) in terms of compensation for harm caused to the life or health of each victim, 500 thousand rubles;
b) in terms of compensation for damage caused to the property of each victim, 400 thousand rubles.
A change in the amount of the insured amount, within which the Insurer, upon the occurrence of each insured event (regardless of their number during the term of the Contract), undertakes to compensate the injured for the damage caused, entails a change in the amount of the insured amount specified in this Contract, in accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation ...
11.5. The relations of the Parties not regulated by this Contract are subject to the norms of the current legislation of the Russian Federation.
11.6. The Contract enters into force from the date of its conclusion and terminates from the date of expiration of the last insurance policy ________________ (28), but not earlier than the Parties fulfill their obligations under the Contract in full.
_________________________
(28) The term of the expiration date of the Contract may be changed if necessary.
11.7. Document circulation within the framework of the Contract is carried out in writing. For prompt notification, it is allowed to exchange documents by facsimile (telephone) communication, e-mail with the obligatory sending (transfer) of the original document within 3 (three) working days.
11.8. The term for responding to an incoming document under the Contract cannot exceed 5 (five) business days from the date of its receipt.
11.9. The contract has been drawn up in accordance with the requirements of the legislation of the Russian Federation and signed by duly authorized representatives of the Parties.
11.10. During the performance of the Contract, it is not allowed to change the Insurer, unless new insurer is the legal successor of the Insurer under the Contract due to the reorganization of a legal entity in the form of transformation, merger or accession.
11.11. All attachments to the Contract must be drawn up in accordance with the current legislation of the Russian Federation and signed by duly authorized representatives of the Parties. All attachments, drawn up in proper form and in accordance with the terms of the Contract, are its integral part.
11.12. The insurer is obliged to provide the Insured with information about the change of its address no later than 2 (two) business days from the date of the corresponding change. In case of failure to provide a notification within the specified period, the address indicated in the Contract will be considered the address of the Insurer.
If the Insurer changes phone numbers, fax numbers, e-mail addresses, bank details for settlements under the Contract, the Insurer must notify the Insured about this within 24 hours from the date of the changes. In case of failure to provide within the prescribed time period a notification of the change in the specified information by phone numbers, faxes, e-mail addresses, bank details for settlements under the Contract, the information specified in the Contract will be considered.
12. Annexes to the contract
12.1. Appendices to the Contract are its integral parts:
Appendix 1 - List of vehicles.
Appendix 2 - Price formula.
Appendix 3 - Document confirming the security for the execution of the Contract. (29)
_________________________
(29) An appendix is included in this clause if there is a section on securing the execution of the Contract in the draft Contract.
13. Addresses and details of the parties
13. ADDRESSES AND DETAILS OF THE PARTIES:
Policyholder: | Insurer: |
Appendix 1 to the government contract
Annex 1
for the provision of services for compulsory
liability insurance
vehicle owners (OSAGO)
List of vehicles
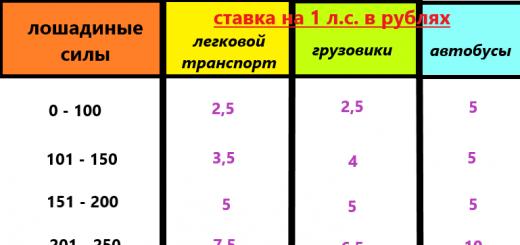
An identification number | Year of manufacture | Engine power, h.p. | State registration plate | Territory of preferential use | Insurance date | Insurance period | |||||
Appendix 2 to the government contract
Appendix 2
to the state contract (contract)
dated ___________ 20___ No. _______
for the provision of services for compulsory
liability insurance
vehicle owners (OSAGO)
Price formula
Price formula:
The maximum value of the Contract price set in the procurement documentation consists of the amount of insurance premiums for each vehicle specified in Appendix No. 1 to the Contract.
The amount of the insurance premium is calculated in accordance with clause 2 of the Procedure for the application of insurance rates by insurers when determining the insurance premium under a compulsory insurance contract (Appendix No. 4 to the Ordinance of the Central Bank of the Russian Federation dated September 19, 2014 No. insurance rates, requirements for the structure of insurance rates, as well as the procedure for their application by insurers when determining the insurance premium for compulsory civil liability insurance of vehicle owners "according to the formula:
(30)
_________________________
(30) The required variant of the formula for calculating the insurance premium (s) is indicated.
Where:
T is the size of the insurance premium;
TB is the base rate of the insurance tariff;
КТ - coefficient of insurance rates depending on the territory of the preferential use of the vehicle;
KBM - coefficient of insurance rates, depending on the presence or absence of insurance claims upon occurrence of insured events that occurred during the period of validity of previous contracts (agreements) of compulsory insurance;
KO - coefficient of insurance rates, depending on the availability of information on the number of persons allowed to drive a vehicle;
КМ - coefficient of insurance rates depending on the technical characteristics of the vehicle, in particular, the engine power of a passenger car (vehicles of categories "B", "BE");
CRC - coefficient of insurance rates, depending on the presence in the Compulsory Insurance Contract of a condition providing for the possibility of driving a vehicle with a trailer to it;
КС - coefficient of insurance rates depending on the period of use of the vehicle;
KP - coefficient of insurance rates depending on the period of insurance;
КН - in the presence of violations provided for by paragraph 3 of Article 9 of the Federal Law of April 25, 2002 No. 40-FZ "On compulsory insurance of civil liability of vehicle owners", the КН coefficient is applied - 1.5.
Maximum value of the Contract price
Model, vehicle brand | Vehicle plate number | |||||||||||
Total: | ||||||||||||