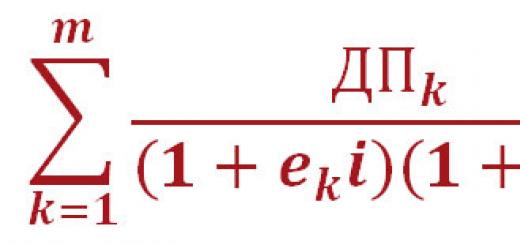1 slide

2 slide
An economic system is an ordered set of socio-economic and organizational relations between producers and consumers of goods and services. economic system

3 slide
Various criteria can underlie the selection of economic systems: the economic state of society at a certain stage of development (Russia in the era of Peter I, Nazi Germany); stages of socio-economic development (socio-economic formations in Marxism); economic systems characterized by three groups of elements: spirit (the main motives of economic activity), structure and substance in the German historical school; types of organization associated with ways of coordinating the actions of economic entities in ordoliberalism; socio-economic system based on two features: the form of ownership of economic resources and the way in which economic activity is coordinated.

4 slide

5 slide
Traditional economy based on the dominance of traditions and customs in economic activity. an economic system in which the distribution of limited resources occurs in accordance with customs; the pace of change and development in it is extremely low; people do what their parents used to do; most of the goods are consumed where they are produced Elements of the traditional economy are found in the most remote areas of the world: in isolated tribes or groups (peoples of the Far North, peoples of Africa) Traditional economic system

6 slide
The command economy is due to the fact that most enterprises are state-owned. an economic system in which resources are state property; the most important decisions affecting the distribution of resources are made by government agencies Typical countries with a command economy system: Cuba, North Korea, Vietnam, China, Albania, USSR, countries of Eastern Europe Command economic system

7 slide
The market economy is defined by private ownership of resources, the use of a system of markets and prices to coordinate and manage economic activity. economic system in which economic decisions at the national level are the result of decisions made by individual sellers and buyers in the market Market economic system is typical for countries: Argentina, India, Turkey, Indonesia and others Market economic system

8 slide
A mixed economy is an economic system where both the state and the private sector play an important role in the production, distribution, exchange and consumption of all resources and material goods in the country. an economic system that combines elements of public ownership of the means of production with private ownership A mixed economic system is characteristic of most countries in modern world: Japan, Sweden, USA, Canada, Finland and others. There are five main tasks solved by a mixed economy: providing employment; full use of production capacity; price stabilization; parallel growth of wages and labor productivity; equilibrium of the balance of payments. mixed economy

9 slide
transitional economy- the economy, which is in a state of change, transition from one state to another, both within one type of economy and from one to another type of economy, occupies a special place in the development of society. At present, various approaches to the study of transitional processes occurring in the economies of post-socialist countries are being proposed. The complexity and versatility of the problem of transition (transformation) of the economy from one type to another, according to a number of authoritative researchers, lies both in the deep root foundations of individual transformation processes and in their interaction. transitional economy

10 slide
Summing up, we note that economic systems multidimensional. They can be formalized: ES = f(A1, A2, A3 ... An). In other words, an economic system (ES) is defined by its properties (A), where there are n such properties. This means that an economic system cannot be defined in terms of a single characteristic.
slide 1
Topic of the consultation: "Types of economic systems"
Tomskaya Zh.V., teacher of the highest category, MBOU secondary school No. 7
slide 2

Distribution of tasks by parts of work
Part of the work Number of tasks Maximum primary score % of the maximum primary score from the tasks of this part from 59 Type of tasks
Part 1 20 20 33.9 Multiple choice
Part 2 8 13 22.0 Short answer
Part 3 9 26 44.1 Long answer
Total 37 59 100
slide 3

The economic system is an established and operating set of principles, rules, laws that determine the form and content of the main economic relations that arise in the process of production, distribution, exchange and consumption of an economic product. (Products and service)
slide 4

The type of economic system is characterized by: forms of ownership, ways of distributing limited resources; ways of regulating the economy.
slide 5

The main questions of the economy:
What to produce? How to produce? For whom to produce?
slide 6

Mixed economy - a way of organizing economic life, in which land and capital are privately owned, and the distribution of limited resources is carried out both by markets and with significant state participation.
Slide 7

1.What to produce Products Agriculture, hunting, fishing. Few products and services are produced. What to produce is determined by customs and traditions that change slowly Determined by groups of professionals: engineers, economists, computer specialists, industry representatives - "planners" Determined by consumers themselves Producers produce what consumers want, i.e. what can be bought
Slide 8

Lines of comparison Traditional Centralized (command and administrative, planning) Market
2. How to produce? They produce in the same way as and with what their ancestors produced. Determined by the plan. Determined by the producers themselves.
Slide 9

Lines of comparison Traditional Centralized (command and administrative, planning) Market
3. For whom to produce? Most people exist on the brink of survival. The surplus product goes to the chiefs or landowners, the rest is distributed according to custom. "Planners", directed by political leaders, determine who and how much will receive goods and services. Consumers get what they want, producers get profit
Slide 10

Social market economy model
Market State
Directs production to meet the growing and changing needs of people Contributes to an increase in the cost of human development Assumes the coexistence of various forms of ownership Acts as a social guarantor of stability Protects people in a market economy
slide 11

Lines of comparison Traditional Centralized (command and administrative, planning) Market
Definition A method of organizing economic life based on backward technology, widespread manual labor, a multi-structural economy A method of organizing economic life in which capital and land, almost all economic resources are owned by the state A method of organizing economic life in which capital and land are in private property of individuals
slide 12

Own
Own
Private
Public
Property of citizens Property of legal entities created by them
State property Municipal property
slide 13

The main forms of economic organization of production:
Subsistence economy - an economy in which people produce products only to satisfy their own needs, without resorting to exchange, to the market Commodity economy - an economy in which products are produced for sale, and the connection between producers and consumers is carried out through the market
Centralized (command), market and mixed economies Traditional economy
Slide 14

Advantages of a planned (command) economy:
Focus on creating a satisfactory standard of living for all (provided a low, but relatively standard of living, but relatively satisfactory for all people). Price stability. Timely payment of wages. Confidence in the future. The absence of a colossal gap in the incomes of citizens and the enrichment of a small part of families at the expense of the impoverishment of other members of society. No unemployment. A higher degree of social protection of citizens from the state. Free and accessible for all basic services (medical, educational).
slide 15

Disadvantages of a planned (command) economy:
Lack of opportunity for manufacturers of goods to make their own business decisions. The obligation of enterprises to strictly fulfill the state plan. The focus on "volume", i.e. on the production of as many goods as possible, and not on the production of quality products. approximate five year plans leading to a shortage of some goods and an excess of others. The receipt by the management of the enterprise of unreasonably high bonuses for overfulfillment of underestimated planned targets. The reluctance of consumers to buy exactly those goods that are produced by domestic enterprises in accordance with the state plan. The emergence of "black" markets for the sale of scarce goods at speculative prices. Solving the shortage problem with the help of special stores and a coupon-card system. Low quality goods. Weak introduction of advanced production technologies due to its focus on the plan, not profit. Low level of agricultural development. Food problem. Too expensive administrative apparatus, which should monitor the implementation of the state economic plan. State support even for those enterprises that bring losses, produce goods that are not in consumer demand.
slide 16

Advantages of a market economy:
Greater freedom of choice for producers and consumers. A large apparatus of officials is not needed to manage the economy. Providing consumers with the goods they need. A wide range of goods and services. Constant focus on search modern methods the production of new goods, the introduction of new technologies that provide high quality products and high profits for firms. The impact of competition between firms on the efficiency of their work, on reducing prices and improving the quality of goods and services. Lack of shortages due to the quick response of entrepreneurs to consumer requests. High productivity of farms due to private ownership of land.
To use the preview of presentations, create a Google account (account) and sign in: https://accounts.google.com
Slides captions:
Command and mixed economic systems
Plan: Command economic system. Mixed economic system. Socially regulated market. Economic system in modern Russia.
Command economic system This is a way of organizing economic life in which capital and land are owned by the state, and the distribution of limited resources is carried out according to the instructions of the central government and in accordance with plans.
The heyday of the command economy was after the First World War. An example of a country in the 20th century with a command economic system was Soviet Russia.
The activities of the command economic system were as follows: What to produce - established by the State Planning Department; How to produce - was established by the sectoral ministry; To whom to sell - installed State Committee for supply; At what price to sell - set the State Committee on Pricing; How much to pay workers - established the State Committee for Labor and wages; How to use income - established by the Ministry of Finance; What to build for production - established the State Committee for Construction; What to sell abroad and buy was established by the Ministry of Foreign Trade.
Planning in a command economic system is very intelligent. The plan must: Be drawn up on the instructions of a private owner who bears full financial responsibility; Be implemented on the basis of a free choice of partners in the transaction; To be checked for reasonableness by the demand of buyers; Rely on existing economic information.
Mixed economic system This is a way of organizing economic life based on the use of various forms of ownership, in which the distribution of limited resources is carried out by markets, and with significant state participation.
A mixed economic system prevailed for the civilizations of the late twentieth century. The basis of a mixed economic system is private ownership of economic resources.
Some countries have a public sector. It includes enterprises whose capital is wholly or partly owned by the state, but which: Do not receive plans from the state; I work according to market laws; Forced to compete on an equal footing with private firms.
The main elements of a mixed economic system:
A socially regulated market This is a kind of mixed economic system in which society and the state are clearly striving not only to ensure economic growth, but also to fully implement the principles of combining economic freedom, reasonable distribution of responsibility for the life of society between citizens and the state, and civil solidarity.
The basis of the mixed economic system is the conscious life position of every able-bodied citizen - "I am responsible for my well-being myself!"
In Modern Russia: The Basics command system destroyed; The mechanism of the market system is still being formed; Factors of production have not yet been completely transferred to private ownership. In the near future, Russia will inevitably have to recreate market mechanisms and build a mixed economic system on their basis.
Thank you for your attention The presentation was prepared by Anzhelika Alexandrovna Danilchuk, a teacher of economics at MBOU Secondary School No. 5 in Kashin
On the topic: methodological developments, presentations and notes
Mathematics lesson in grade 3 according to the Zankov system on the topic "Fractions. Converting a mixed number to an improper fraction" + presentation. Arginskaya's textbook ...
Economic game "Economic cafe" 2010.
Material for the economic game "Economic Cafe": game rules, presentation, menu samples ....
Time has changed a lot. The country is in motion. The world of human knowledge, which is rapidly developing on the threshold of the third millennium, now and then throws you to school education...