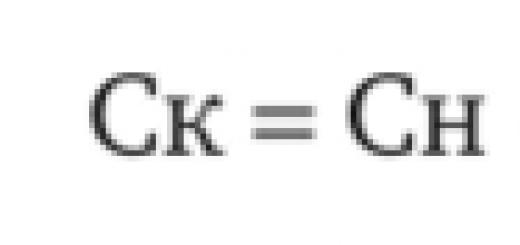Description of the presentation on individual slides:
1 slide
Description of the slide:
2 slide

Description of the slide:
Task 1 The company "Konus" decided to expand production by increasing the range of goods. The output of products and required the following total costs: raw materials - 500 thousand rubles, wage workers - 100 thousand rubles, fuel - 70 thousand rubles, transport services - 7 thousand rubles, expenses for training and retraining of personnel - 6 thousand rubles, deductions for property insurance - 1 thousand rubles. Calculate the sum of fixed and variable costs.
3 slide

Description of the slide:
Task 2 The owner of the company paid employees 50 thousand rubles. The interest payment for the loan amounted to 100 thousand rubles; depreciation deductions - 50 thousand rubles; the cost of raw materials, heating, lighting, repairs - 30 thousand rubles. The total income of the company amounted to 300 thousand rubles. The owner of the company can get a job as an employee in another company and receive 60 thousand rubles there. From investing his capital in another enterprise, the owner of the company could receive 20 thousand rubles. Determine: 1) Accounting and economic costs; 2) Accounting and economic profit; 3) Should the business owner continue his business?
4 slide

Description of the slide:
Task 3 A furniture factory produces beds. She set as her goal to achieve a profit of 15,000 rubles. per month. The price of one bed is 400 rubles, the average variable costs are 150 rubles. Fixed costs amount to 4000 rubles per month. a) determine how many beds the company should produce per month b) how many beds the company will produce if the price rises to 500 rubles.
5 slide

Description of the slide:
Task 4 At a price of 60 rubles. per copy, the publishing house sells 10,000 copies of its glamorous magazine. If the price drops to Rs. per copy, 20 thousand copies will be sold already. The total costs of the publishing house with the previous circulation amounted to 300 thousand rubles. , and with a new circulation they will amount to 700 thousand rubles. By how much will the publisher's profit increase as a result of the price reduction?
A large car factory and a small shoe repair shop, tourist agency and a chain of restaurants can be called in one word - a firm. It is firms that act in the markets of goods and services as sellers offering their products.
Firm
in economics (enterprise) is a commercial organization that incurs costs economic resources to produce goods and services for sale on the market.
The owner of the company seeks to organize its activities in such a way as to receive income from the sale of goods or services in the form of profit. Achieving this goal largely depends on the rational choice of the type and volume of goods produced, production technology, skillful combination and use of the main production resources, competent management of the production process and marketing of finished products on the market.
As you can see, the set of tasks is quite wide and varied, and their solution does not promise success to everyone. Many entrepreneurial ventures often fail. In countries with developed market economies, not only do dozens of new firms are born every day, but no less number of them go bankrupt.
What can help the manufacturer achieve efficient production and ensure the viability of the firm? The materials under study and the next two paragraphs are devoted to finding an answer to this question.
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION AND FACTOR INCOMES
The production process is the transformation of economic resources (factors of production) into goods and services. The factors of production are: labor (workers and their qualifications), land (land plot on which the enterprise is located, raw materials), capital (industrial building, machines, tools).
The economic prosperity of any company is ensured not only by the named resources - labor, natural, capital. No less important is another factor that binds together all the others - entrepreneurial ability. Entrepreneurs direct their organizational and managerial efforts to make the best use of available production resources. This will allow them to achieve high results (more products of better quality) and, if successful, profit.
You already know that all resources in the economy are limited, that is, they are not enough to produce as many goods as people would like. For the economy to function properly, producers must learn to make choices from limited resources. If a firm builds a house for its employees, then the resources available to it (building materials, workers, construction equipment) can no longer be simultaneously used to repair its administrative building. The government, with a limited budget, may delay the construction of several schools in order to use the funds to repair heavy traffic roads. As a result of choice, you have to give up something in order to get something else in a more complete way.
Each factor of production has a specific owner. The owner of a factor of production should receive compensation or payment for the fact that someone with his consent uses his resource. Each of us owns at least one of the factors of production (labor, land, capital, entrepreneurial ability) that can generate income. The amount of this income depends on the quantity and quality of the factor of production that you own. If you own only a certain specialty and health, then you receive remuneration for your work in the form of wages. Among participants in the modern economy, this source of income is the most common.
Suppose you own only such a factor of production as entrepreneurial ability. To organize production, you will have to use other people's factors of production: rent land, machinery and equipment, hire workers, take out financial resources on credit. By selling the manufactured products, you can pay part of the proceeds to the owners of the factors of production. Part of the proceeds will remain with you in the form of profit. Profit will be a reward for your efforts and a payment for your entrepreneurial abilities.
The income generated by a factor of production such as land is called rent. The owner of the land may not carry out entrepreneurial activities and not make additional efforts to use it. For example, you, owning a plot of land, can lease it to other persons for temporary use on contractual terms, for a fee. This fee will be your income from the use of the land.
Capital (from lat. capitalis - main) - property that can generate income. Capital is a source of income invested in a business in the form of means of production. If the firm can hire labor, lease land, then the capital usually belongs to it.
Please note that the concept of "capital" has several meanings: physical capital (means of production created by people for the production of goods and services), monetary or financial capital (money used to acquire physical capital), investment (investment of material and cash for production).
Real, fixed capital is the means of production in the form of machines, tools and other production equipment. Money as such does not produce anything, it can be used to purchase various means of production. Money used or intended for the acquisition of physical capital (invested in production) should bring income to its owner in the future.
During the production process, temporarily free cash at the expense of: deductions for the repair and replacement of worn-out means of labor; formed as a result of a temporary gap between the receipt of money from the sale of goods and the payment of wages; part of the profit accumulated for the expansion of production, etc. The inactivity of temporarily free cash contradicts the very nature market economy, "unemployed money" reduces the efficiency of production, reduce the return on capital. They can be used as loan capital - temporarily free cash provided on a loan on terms of repayment and payment. Income on loan capital is the interest paid by borrowers for the use of other people's money.
The income of the owners of factors of production is at the same time the costs of the owner of the enterprise (firm). Therefore, the efficiency of the company's production activities largely depends on the rational combination and use of attracted and own factors of production.
How to determine how effective the economic activity of the company? For this, it is necessary, in particular, to compare the results of work with costs (costs, expenses).
ECONOMIC AND ACCOUNTING COSTS AND PROFIT
As noted above, the activity of the company makes sense for its owner only if it makes a profit. Recall that profit appears as a result of the excess of revenue from the sale of products over the sum of costs for all factors of production for this activity. Thus, any firm, releasing products, must cover its costs. Otherwise, its owner will face losses and ruin.
production costs
- this is the cost of the producer (owner of the firm) for the acquisition and use of factors of production.
For an enterprise (company) economic costs
- these are the payments that the company must make to suppliers of the necessary resources (labor, material, energy, etc.) in order to divert these resources from use in other industries. These payments are divided into internal and external, and various approaches are used in their calculation.
Internal (or implicit) costs
is the cost of resources owned by the owner of the firm. For example, the premises in which the company is located is the property of its owner; the owner of the firm uses his own labor as a manager. Since these resources are owned by the firm itself, there will be no external costs (rental of premises, wages of a hired manager), but, from the point of view of the firm, these internal costs are equal to cash payments that could be received for own resources with an alternative use of them. (best possible). Thus, one's own premises could be rented out, and the owner of the company, not receiving a satisfying income, could receive income in the form of a salary by working for hire.
That is why remuneration for the performance of entrepreneurial functions is called normal profit and is included in internal costs. Internal costs are often hidden, implicit in nature, but they must be taken into account when making economic decisions. And if the accountant fixes the costs incurred, trying to calculate what the production of products will cost the company, then the owner of the company solves the problem of economic choice: is it worth continuing your business or is it better to find a more profitable option for using your own resources.
External costs
is the payment for factors of production that are not the property of the owner of the firm. These include costs for materials, energy, labor services, etc. e. External costs are obvious and reflected in accounting documents, so they are called accounting or explicit costs.
Thus, economic costs include external (accounting, or explicit) and internal (implicit) costs with normal profit included in the latter. It is the payment for resources required to attract and retain them in a given activity (use case).
Differences between economic and accounting costs inevitably lead to different definitions of profit.
Economic profit is the difference between a firm's total revenue and economic costs.
This approach to profit makes it possible to assess the possibility of the existence of the enterprise (whether the revenue covers not only external, accounting, but also internal costs, including normal profit). The excess of cash receipts of the sum of economic costs means that the enterprise has a net profit, its existence is justified, it can develop successfully.
Accounting profit is the difference between total revenue and accounting costs.
Economic profit directs the entrepreneur not just to earn income, but to compare this income with that which could be obtained as a result of an alternative use of available resources. For example, an entrepreneur, having organized production, received an accounting profit of 3000 rubles. And if he put money in the bank, he would receive 4000 rubles. as a percentage. Hence, if the accounting profit turns out to be less than the economic profit, taking into account opportunity costs, then the use of the resource should be considered inefficient from the point of view of the entrepreneur.
Different understanding of the profit of the firm by economists and accountants leads to different conclusions about the state of affairs in the firm.
What method of calculating costs - accounting or economic - is it better for an entrepreneur to use when analyzing not only the efficiency of his production, but also the prospects for its development? Probably, to calculate the actual value of costs and profits, the accounting method should be used. For making decisions on the choice of one of the alternative options for investing resources, only the economic method of calculating costs is acceptable.
Any owner of the enterprise aspires to increase - the sizes of profit. For the sake of this, he improves the technology and organization of production, stimulates an increase in the productivity of workers, and introduces a mode of saving resources. This leads to a reduction in the value of all costs and contributes to the growth of profits.
When calculating production costs, the owner of the company must take into account their various types. Let's get acquainted with the costs that are most significant for accounting by the manufacturer.
FIXED AND VARIABLE COSTS OF PRODUCTION
Costs are formed differently depending on the type of resources used in production. Consider them using the example of the use of materials and production facilities of an enterprise for the manufacture of washing machines. The more units of production are made, the more material is spent, therefore, the costs associated with the use of materials (metal, plastic, rubber) will increase. At the same time, the dimensions of the building and workshops, the volume of equipment do not change, which means that the costs associated with the use of the building and the equipment installed in the workshops may remain the same. Such differences in the use of productive resources led economists to consider such types of costs as fixed and variable.
fixed costs - this is that part of the total costs that does not depend at a given point in time on the volume of output.
An example of a fixed cost would be the company's rent for the premises, the cost of maintaining the building, the cost of training and retraining of personnel, salaries of management personnel, utility costs, depreciation.
Depreciation - decrease in the cost of capital resources as they wear out in the process of production use. To compensate for the wear and tear of buildings, equipment, Vehicle money is accumulated (depreciation deductions), which are directed to the repair or manufacture of new means of labor instead of worn ones. These deductions are included in fixed costs.
A company incurs fixed costs even if it is not operating. For example, if a bakery temporarily stopped the production of its products, then all the same, utilities, salaries of management personnel will require expenses.
variable costs - this is that part of the total costs, the value of which for a given period of time is directly dependent on the volume of production and sales of products.
Examples of variable costs are the cost of acquiring raw materials, labor, energy, fuel, transport services, packaging and packaging costs, etc.
Variable costs increase as output increases and decrease as output decreases.
The difference between fixed and variable costs is essential for every entrepreneur. He can manage variable costs, as their value changes over a short period of time as a result of changes in the volume of production. Fixed costs are beyond the control of the company's administration, as they are mandatory and must be paid regardless of the volume of production.
The analysis of changes in production costs depending on the volume of output is very important. Only on its basis can one understand how firms make decisions and determine the volume of production of goods and services, as well as set prices for goods offered on the market. Comparison of production costs is extremely important for the management of the firm, determining the optimal size of production and opportunities for obtaining sustainable income.
So, business participants who want to make their business efficient have to think about increasing profits and reducing costs. All of the above will help answer one more question: what does an efficient business mean, an efficient enterprise (firm)? And although the concept of "efficiency" has already been used, let's try to better understand it.
The concept of "efficiency" comes from the word "effect". In economics, an effect is a specific positive result of some activity (for example, an increase in profits received by a company compared to the previous year, or the amount of money saved). Efficiency is determined by comparing the magnitude of the effect and the costs (costs, expenses) that ensure its receipt.
Efficiency - the effectiveness of the process, defined as the ratio of the effect, result to costs. To analyze the efficiency and profitability of an enterprise, such an indicator as profitability is used. Profitability is calculated as the ratio of the profit received by the enterprise for a certain period to the costs incurred during the same period (profitability = profit:costs) Think about what needs to be done to achieve high efficiency of the company.
TAXES PAID BY ENTERPRISES
The amount of profit of the enterprise is influenced not only by the costs of production, but also by the amount of taxes paid by it. Taxes are a significant cost item for the manufacturer, which he has to take into account when organizing and running his business.
You got acquainted with the tax system in elementary school. Recall that taxes are divided into direct and indirect. Direct taxes are levied explicitly on the income of citizens and firms (for example, income tax, income tax, property tax). Indirect taxes are paid imperceptibly when performing certain actions (for example, when buying a product, exchanging currency, importing goods from abroad) and included in the cost of goods and services (for example, sales tax, customs duty) are paid by consumers.
What types of taxes are paid by modern enterprises?
Direct corporate tax - Income tax is widely used in world practice. In Russia, the law provides for the taxation of the profits of all enterprises and organizations, in a number of countries this tax is paid only by joint-stock companies, and small enterprises and partnerships pay income tax. In most cases, income tax is 35% of gross profit, i.e. the difference between all income and all expenses of the firm. The income tax rate may vary depending on the type of activity. Thus, income from banks, insurance companies, stock exchanges and from intermediary activities is taxed at a rate of 43%, and income from casinos and gambling business - at a rate of 90%. But there are also tax incentives that allow the government to incentivize actions that are beneficial to society. In Russia, for example, part of the profit used for investments in the development of production, scientific research, and charity events is partially exempt from tax. Profit received from the production and sale of agricultural products is not subject to taxation.
Indirect corporate tax - value added tax (VAT). It was invented by economists not so long ago (first introduced in the 60s of the XX century), but today it is used by about 50 countries. In Russia, this tax was introduced in 1992 and is a key tax in the tax system. Thus, more than a third of the revenue part of the federal budget is formed from the proceeds of this tax.
Value added tax is imposed on the increase in the value of the goods, which is created at all stages of its production as the goods move to the final consumer (from raw materials to consumer goods). For each firm, taxation of its proceeds from the sale of products is established, minus the amount of costs for raw materials, materials, equipment and other material costs.
In Russia in 2004 the value added tax rate was set at 18%, and for certain goods (essential food products, goods for children) - at 10%. Compare these figures with the VAT level in other countries (France - 18.6%, England - 15%, Germany - 14%, Luxembourg - 12%). Think about how the level affects this indicator. economic development country, economic policy states.
The entrepreneur also has to make payments to various off-budget funds (pension, social insurance, compulsory health insurance and etc.). These contributions, from his point of view, are also taxes.
Practice confirms that high stakes taxes reduce the motivation for active work, in general, business activity. The American economist Laffer theoretically proved that at the rate income tax more than 59% sharply reduced entrepreneurial activity.
Each government is forced to solve the problem of finding the best possible option for taxing enterprises so that they have the necessary funds to develop and expand their production.
PRACTICAL CONCLUSIONS
1 Knowledge of the conditions and methods for the effective organization of production activities will allow you to become its active and effective participants. It should be remembered that the success of this activity depends not only on your abilities (organizational, intellectual), but also on the skillful use of the limited resources available.
2 Each of us owns one or more factors of production. We must try to find ways and ways to use them rationally and generate income.
3 To make a decision about organizing your own business, you need to analyze and compare future costs and possible income from future activities. This will make it possible to make an economically sound choice of the use of available resources and reduce the likelihood of losses and ruin.
DOCUMENT
How the market regulates the costs and results of production. From the book of a modern Russian economist V. I. Danilova-Danilyana
"Running to the Market".
The market regulates costs and results in such a way that, in general terms, they turn out to be approximately proportional for each expedient production. If the results of some manufacturer outstrip the costs, then, according to the classical scheme, others rush into this area of activity. This leads to an increase in supply, a fall in the prices of the corresponding products, and a standard cost-benefit ratio is established. If, on the contrary, somewhere the costs begin to overtake the results, then such a producer goes bankrupt, the production facilities belonging to him are closed. What is unprofitable - does not survive, what is super-profitable - becomes the area of application of new forces, the balance of costs and results is restored in both cases. This classical scheme, developed by A. Smith, does not always accurately reflect real processes, but in principle remains true. Even in the situation of a monopoly producer, strong pressure arises, leading to changes of the type described, to weakening the revealed excess of private efficiency over the average.
QUESTIONS AND TASKS FOR THE DOCUMENT
1. Explain, based on the text of the fragment, how the market regulates the costs (costs) and results of production. Describe the behavior in the market of a manufacturer interested in the success of his production. What determines their profit?
- Knowing the conditions and methods for the effective organization of production activities will allow you to become its active and effective participants. It should be remembered that the success of this activity depends not only on your abilities (organizational, intellectual), but also on the skillful use of the limited resources available.
- Each of us owns one or more factors of production. We must try to find ways and means of their rational use and income generation.
- To make a decision about organizing your own business, you need to analyze and compare future costs and possible income from future activities. This will make it possible to make an economically sound choice of the use of available resources and reduce the likelihood of losses and ruin.
The documents
How the market regulates the costs and results of production. From the book of the modern Russian economist V. I. Danilov-Danilyan "Escape to the Market".
The market regulates costs and results in such a way that, in general terms, they turn out to be approximately proportional for each expedient production. If the results of some manufacturer outstrip the costs, then, according to the classical scheme, others rush into this area of activity. This leads to an increase in supply, a fall in the prices of the corresponding products, and a standard cost-benefit ratio is established. If, on the contrary, somewhere the costs begin to overtake the results, then such a producer goes bankrupt, the production facilities belonging to him are closed. What is unprofitable - does not survive, what is super-profitable - becomes the area of application of new forces, the balance of costs and results is restored in both cases. This classical scheme, developed by A. Smith, does not always accurately reflect real processes, but in principle remains true. Even in the situation of a monopoly producer, strong pressure arises, leading to changes of the type described, to weakening the revealed excess of private efficiency over the average.
Questions and tasks for the document
- Explain, based on the text of the fragment, how the market regulates the costs (costs) and results of production. Describe the behavior in the market of a manufacturer interested in the success of his production. What determines their profit?
- The well-known Austrian economist Josef Schumpeter called the mechanism of the market ousting old goods, technologies, ideas that do not bring profit, and replacing them with new ones, "the system of creative destruction." Think why.
- Discuss the causes and consequences of such a mechanism, using the text of the document and the materials of the paragraph.
- Can the market be called the only tool for objective social comparison of costs and results of production? Justify your answer.
Questions for self-examination
- What determines the success of an enterprise?
- What income can be obtained by owning the factors of production?
- Is it possible and how to get income without capital?
- Why does a manufacturer calculate costs and profits?
- What is an "efficient enterprise"?
- What taxes do firms pay?
Tasks
- Make a list of the costs that are necessary in order to: open a household appliance repair shop, organize a gala dinner in a cafe for thirty people, open a sports equipment rental office.
- The growth in demand for the products of the printing plant required an increase in production. Which production costs will be decisive: fixed or variable?
- The company "Konus" decided to expand production by increasing the range of products. The output of products required the following total costs: raw materials - 500 thousand rubles, wages of workers - 100 thousand rubles, fuel - 70 thousand rubles, transport services - 7 thousand rubles, expenses for training and retraining of personnel - 6 thousand rubles, deductions for property insurance - 1 thousand rubles. Calculate the sum of fixed and variable costs.
- The value of the enterprise's profit per year amounted to 100 million rubles, and production costs - 60 million rubles. Calculate the profitability of its activities. Explain whether and why this production can be considered expedient from an economic point of view.
Thoughts of the wise
"The optimism of an entrepreneur is the driving force of economic enterprise, prudence is the power of his self-preservation."
G. K. Gins (1887-1971), Russian writer, jurist
Lesson in social science on the topic "Firm in Economics"
Purpose: to consider the basic principles of the company's activity in the economy.
Subject: social science.
Date: "____" ____.20___
I.Message about the topic and purpose of the lesson.
II. Presentation (with elements of conversation) of the program material.
Why do some firms succeed while others fail? Is it profitable to produce everything? Are there recipes for bankruptcy? Can unprofitable enterprises exist in a market system?
A large car factory and a small shoe repair shop, a travel agency and a chain of restaurants can be summed up in one word - a firm. It is firms that act in the markets of goods and services as sellers offering their products.
Firm in economics (enterprise) is a commercial organization that spends economic resources for the manufacture of goods and services sold on the market.
The owner of the company seeks to organize its activities in such a way as to receive income from the sale of goods or services in the form of profit. Achieving this goal largely depends on the rational choice of the type and volume of goods produced, production technology, skillful combination and use of the main production resources, competent management of the production process and marketing of finished products on the market.
As you can see, the set of tasks is quite wide and varied, and their solution does not promise success to everyone. Many entrepreneurial ventures often fail. In countries with developed market economies, not only do dozens of new firms are born every day, but no less number of them go bankrupt.
What can help the manufacturer achieve efficient production and ensure the viability of the firm? The materials under study and the next two paragraphs are devoted to finding an answer to this question.
Factors of production and factor income
The production process is the transformation of economic resources (factors of production) into goods and services. The factors of production are: work(employees and their qualifications), Earth(land plot on which the enterprise is located, raw materials), capital(industrial building, machines, tools).
The economic prosperity of any company is ensured not only by the named resources - labor, natural, capital. No less important is another factor that binds together all the others - entrepreneurial ability. Entrepreneurs direct their organizational and managerial efforts to make the best use of available production resources. This will allow them to achieve high results (more products of better quality) and, if successful, profit.
You already know that all resources in the economy are limited, that is, they are not enough to produce as many goods as people would like. For the normal functioning of the economy, producers must learn to make choices from limited resources. If a firm builds a house for its employees, then its resources (building materials, workers, construction equipment) can no longer be simultaneously used to repair its office building. The government, with a limited budget, may delay the construction of a few schools in order to use the funds to repair high-traffic roads. As a result of choice, you have to give up something in order to get something else in a more complete way.
Each factor of production has a specific owner. The owner of a factor of production should receive compensation or payment for the fact that someone with his consent uses his resource. Each of us owns at least one of the factors of production (labor, land, capital, entrepreneurial ability) that can generate income. The amount of this income depends on the quantity and quality of the factor of production that you own. If you own only a certain specialty and health, then you receive remuneration for work in the form of wages. Among participants in the modern economy, this source of income is the most common.
Suppose you own only such a factor of production as entrepreneurial ability. To organize production, you will have to use foreign factors of production: rent land, machinery and equipment, hire workers, take out a loan. By selling the manufactured products, you can pay part of the proceeds to the owners of the factors of production. Part of the proceeds will remain with you in the form of profit. Profit and will be a reward for your efforts and a reward for your entrepreneurial ability.
The income generated by a factor of production such as land is called rent. The owner of the land may not carry out entrepreneurial activities and not make additional efforts to use it. For example, you, owning a plot of land, can lease it to other persons for temporary use on contractual terms, for a fee. This fee will be your income from the use of the land.
Capital(from lat. capitalis- main) - property that can generate income. Capital is a source of income invested in a business in the form of means of production. If labor as a factor of production can be hired by the firm, land can be leased, then the capital usually belongs to it.
Please note that the concept of "capital" has several meanings: physical capital(means of production created by people for the production of goods and services), monetary, or financial, capital(money used to acquire physical capital), investments(investment of material and monetary resources in production, in securities).
Real, fixed capital is the means of production in the form of machines, tools and other production equipment. Money as such does not produce anything, it can be used to purchase various means of production. Money used or intended for the acquisition of physical capital (invested in production) should bring income to its owner in the future.
In the process of production, temporarily free cash is formed at the expense of: deductions for the repair and replacement of worn-out means of labor; formed as a result of a temporary gap between the receipt of money from the sale of goods and the payment of wages; part of the profit accumulated to expand production, etc. The inactivity of temporarily free cash contradicts the very nature of a market economy, "unemployed money" reduces the efficiency of production, reduces the return on capital. They can be used as loan capital - temporarily free funds provided on a loan on a repayment and payment basis. Income on loan capital is the interest paid by borrowers for the use of other people's money.


The income of the owners of factors of production is at the same time the costs of the owner of the enterprise (firm). Therefore, the efficiency of the company's production activities largely depends on the rational combination and use of attracted and own factors of production.
How to determine how effective the economic activity of the company? For this, it is necessary, in particular, to compare the results (profit) with the costs (costs, expenses).
Economic and accounting costs and profits
As noted above, the activity of the company makes sense for its owner only if it makes a profit. Recall that profit appears as a result of the excess of revenue from the sale of products over the sum of costs for all factors of production.
Thus, any firm that produces products must cover its costs. Otherwise, its owner will face losses and ruin.
production costs - This is the cost of the producer (owner of the firm) for the acquisition and use of factors of production.
For an enterprise (company) economic costs - these are the payments that the firm must make to suppliers of the necessary resources (labor, material, energy, etc.) in order to divert these resources from use in other industries. These payments are divided into internal and external, and various approaches are used in their calculation.
Internal (or implicit) costs − is the cost of resources owned by the owner of the firm. For example, the premises in which the company is located is the property of its owner; the owner of the firm uses his own labor as a manager. Since these resources are owned by the firm itself, there will be no external costs (rental of premises, salaries of a hired manager), but, from the point of view of the firm, these internal costs are equal to cash payments that could be received for own resources with an alternative use of them. (best possible). Thus, one's own premises could be rented out, and the owner of the company, not receiving a satisfying income, could receive income in the form of a salary by working for hire.
That is why the reward for performing entrepreneurial functions is called normal profit and is included in internal costs. Internal costs are often hidden, implicit in nature, but they must be taken into account when making economic decisions. And if the accountant fixes the costs incurred, trying to calculate what the production of products will cost the company, then the owner of the company solves the problem of economic choice: is it worth continuing his business or is it better to find a more profitable option for using his own resources.
External costs - This is payment for factors of production that are not the property of the owner of the firm. These include costs for materials, energy, labor services, etc. External costs are obvious and reflected in accounting documents, so they are called accounting or explicit costs.
In this way, economic costs include external (accounting, or explicit) and internal (implicit) costs with normal profit included in the latter. It is the payment for resources required to attract and retain them in a given activity (use case).
Differences between economic and accounting costs inevitably lead to different definitions of profit.
Economic profit - is the difference between the firm's total revenue and economic costs.
This approach to profit makes it possible to assess the possibility of the existence of the enterprise (whether the revenue covers not only external, accounting, but also internal costs, including normal profit). The excess of cash receipts over the value of economic costs means that the enterprise has a net profit, its existence is justified, it can successfully develop.
Accounting profit - is the difference between total revenue and accounting costs.
Economic profit directs the entrepreneur not just to earn income, but to compare this income with that which could be obtained as a result of an alternative use of available resources. For example, an entrepreneur, having organized production, received an accounting profit of 3000 rubles. And if he put money in the bank, he would receive 4000 rubles. as a percentage. Hence, if the accounting profit turns out to be less than the economic profit, taking into account opportunity costs, then the use of the resource should be considered inefficient from the point of view of the entrepreneur.
Different understanding of the profit of the firm by economists and accountants leads to different conclusions about the state of affairs in the firm.
What method of calculating costs - accounting or economic - is it better for an entrepreneur to use when analyzing not only the efficiency of his production, but also the prospects for its development? Probably, to calculate the actual value of costs and profits, the accounting method should be used. For making decisions on the choice of one of the alternative options for investing resources, only the economic method of calculating costs is acceptable.
Any owner of the enterprise seeks to increase the size of profits. For the sake of this, he improves the technology and organization of production, stimulates an increase in the productivity of workers, and introduces a mode of saving resources. This leads to a reduction in the value of all costs and contributes to the growth of profits.
When calculating production costs, the owner of the company must take into account their various types. Let's get acquainted with the costs that are most significant for accounting by the manufacturer.
Value added tax is imposed on the increase in the value of the goods, which is created at all stages of its production as the goods move to the final consumer (from raw materials to consumer goods). For each firm, taxation of its proceeds from the sale of products is established, minus the amount of costs for raw materials, materials, equipment and other material costs.
The entrepreneur also has to make payments to various off-budget funds (pension, social insurance, compulsory medical insurance, etc.). These contributions, from his point of view, are also taxes.
Practice confirms that high tax rates reduce the motivation for active work, in general, business activity. The well-known American economist A. Laffer theoretically proved that with an income tax rate of more than 59%, entrepreneurial activity is sharply reduced.
Each government is forced to solve the problem of finding the best possible option for taxing enterprises so that they have the necessary funds to develop and expand their production.
III. Practical conclusions.
1. Knowledge of the conditions and methods for the effective organization of production activities will allow you to become its active and effective participants. It should be remembered that the success of this activity depends not only on your abilities (organizational, intellectual), but also on the skillful use of the limited resources available.
2. Each of us owns one or more factors of production. We must try to find ways and means of their rational use and income generation.
3. To make a decision about organizing your own business, you need to analyze and compare future costs and possible income from future activities. This will make it possible to make an economically sound choice of the use of available resources and reduce the likelihood of losses and ruin.
IV. Document.
How the market regulates the costs and results of production. From the book modern Russian economist - Danilyan"Escape to the Market".
The market regulates costs and results in such a way that, in generalized terms, they turn out to be approximately proportional for each expedient production. If the results of some manufacturer outstrip the costs, then, according to the classical scheme, others rush into this area of activity. This leads to an increase in supply, a fall in the prices of the corresponding products, and a standard cost-benefit ratio is established. If, on the contrary, somewhere the costs begin to overtake the results, then such a producer goes bankrupt, the production facilities belonging to him are closed. What is unprofitable - does not stand up, what is super-profitable - becomes the area of application of new forces, the balance of costs and results is restored in both cases. This classical scheme, developed by A. Smith, does not always accurately reflect real processes, but in principle remains true. Even in the situation of a monopoly producer, strong pressure arises, leading to changes of the type described, to weakening the revealed excess of private efficiency over the average.
Questions and tasks for the document
1) Explain, based on the text of the fragment, how the market regulates the costs (costs) and results of production. Describe the behavior in the market of a manufacturer interested in the success of his production. What determines their profit?
2) The well-known Austrian economist Josef Schumpeter called the mechanism of the market ousting old goods, technologies, ideas that do not bring profit, and replacing them with new ones, "the system of creative destruction." Think why.
3) Discuss the causes and consequences of such a mechanism, using the text of the document and the materials of the paragraph.
4) Can the market be called the only tool for objective social comparison of costs and results of production? Justify your answer.
V. Questions for self-examination.
1. What determines the success of the enterprise?
2. What income can be obtained by owning the factors of production?
3. Is it possible and how to get income without capital?
4. Why does a manufacturer calculate costs and profits?
5. What is an "efficient enterprise"?
6. What taxes do firms pay?
VI. Tasks.
1. Make a list of the costs that are necessary in order to: open a household appliance repair shop, organize a gala dinner in a cafe for thirty people, open a sports equipment rental shop.
2. The growth in demand for the products of the printing plant required an increase in production volume. Determine which production costs will be critical: fixed or variable.
3. Firm "Konus" decided to expand production by increasing the range of products. The output of products and required the following total costs: raw materials - 500 thousand rubles, wages of workers - 100 thousand rubles, fuel - 70 thousand rubles, transport services - 7 thousand rubles, expenses for training and retraining of personnel - 6 thousand rubles, deductions for property insurance - 1 thousand rubles. Calculate the sum of fixed and variable costs.
4. The amount of profit of the enterprise per year amounted to 60 million rubles, and production costs - 100 million rubles. Calculate the profitability of its activities. Explain whether this production can be considered economically feasible and why.
VII. Thoughts of the wise.
"The optimism of an entrepreneur is the driving force of economic enterprise, prudence is the power of his self-preservation."
(), Russian writer, jurist
VIII. Final part.
1. Evaluation of student responses.
The employment rate of the working-age population in the former USSR at the end of the 1980s was one of the highest in the world: it rose to 95%. In connection withwith this answer the following questions:
1) What does a high level of employment indicate - a low or high level of economic development?
2) Can there be unemployment with a high level of employment? If so, in what form - explicit or implicit?
3) It is known that the growth of employment in the 80s occurred in our country due to the involvement of women in production. Has it positively or negatively affected the birth rate?
.You are the manager of a soft drinks company. In winter, the demand for your products temporarily drops, what measures will you take to reduce productionzhek production all your actions to save production?
Part C.Taxes appear with the emergence of the state, since they are the main source of state revenue. The state must have the means to perform its functions, the main of which are:
Determining the rules for conducting economic activity, the “rules of the game” (antimonopoly law, supporting the development of the private sector of the economy, protecting property rights, protecting freedom of competition, protecting consumer rights, etc.);
Maintaining economic stability (fighting inflation and unemployment, ensuring economic growth);
Production of public goods (ensuring security, law and order, education, healthcare, development of fundamental science);
Social policy (social security for the poor through redistribution of income, payment of pensions, scholarships, unemployment benefits, etc.)
With negative external effects (environmental policy, etc.).
Taxes are the primary means of paying government expenses. Since the services of the state (which, of course, cannot be provided free of charge) are used by all members of society, the state collects fees for these services from all citizens of the country. Thus, taxes are the main tool for redistributing income among members of society and are aimed at reducing income inequality.
The tax system includes:
Subject of taxation (who should pay the tax)
Object of taxation (what is taxed)
Tax rates (the percentage on which the amount of tax is calculated) The amount with which the tax is paid is called the taxable base.
The principles of taxation were formulated by A. Smith in his great work “A Study on the Nature and Causes of the Wealth of Nations”, published in 1776. According to Smith, the tax system should be:
Fair (it should not enrich the rich and impoverish the poor);
Understandable (the taxpayer must know why he pays this or that tax and why he pays it);
Convenient (taxes should be levied when and in a way that is convenient for the taxpayer and not for the tax collector)
Inexpensive (the amount of tax revenue should significantly exceed the cost of collecting taxes).
The basis of modern tax system the principles of fairness and efficiency are laid down. The tax system should ensure the efficient distribution and use of resources at the micro level (the level of an individual producer). Equity must be vertical (meaning that people with different incomes should pay unequal taxes) and horizontal (meaning that people with equal incomes should pay equal taxes).
C2. What elements does the tax system include? Illustrate the operation of the tax system with an example.
C3. Describe any three principles of taxation discussed in the text.