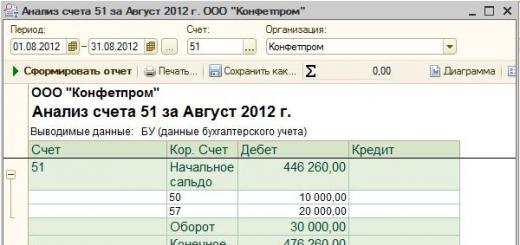
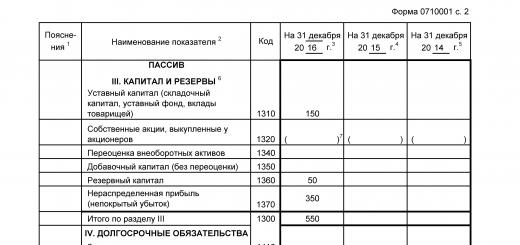
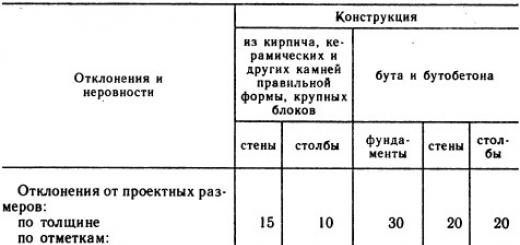
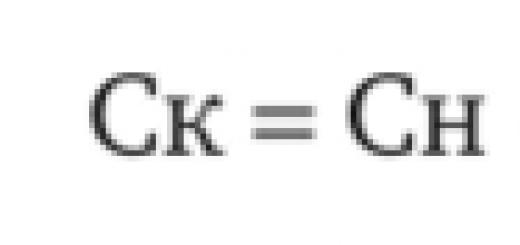Here is the case when parents consider their children to be fools who do not understand anything. You, "protecting the psyche of the child", made the older child suffer, look for his beloved cat, knowing that she had died. Most likely, he was not so stupid, he understood that "it became easier for her, but she ran away from the clinic", most likely, it means that mom is just lying, but logic came into conflict with the still existing trust in her mother, when you think that if mom says something, then she is right - and he understood what happened, but still he continued to wait and hope: “What if she really is alive, because mom can’t lie to me?” And then, when even the youngest told you that he still understands everything (and they probably discussed the case with each other, and more and more came to disappointing conclusions that mom was lying), you also convinced him that he supposedly " not guilty." In my opinion, this is a direct way to raise children who are not able to take responsibility for their actions. I think it would be much more useful here to say that yes, Kusya died because you pushed her, but there's nothing to be done, and now you know that your pampering and experiments can lead to serious consequences, and, of course, you you will never do again. The child would cry and forever remember what he did. A person's personality is made up of memories. And please don't promote mosquito nets as protection against falling cats. They are designed to protect your home from insects, and nothing more. At most, they can protect your parrot from flying out of the window. Here, recently, the news flashed that a one-year-old child fell out with such a net from the 10th, or something, floor ... died, of course. These nets will not protect a cat or a child. They are made of plastic, and are glued with double-sided tape, or pinned with buttons. The slightest load and the grid flies out. The cat can jump onto the net after a bird or a butterfly and fly down. Or maybe just start tearing it, sharpening its claws, and tear it apart. If you start a cat, then buy and install an anti-cat net, this is a metal grill that is firmly attached to the frame with self-tapping screws or bolts, and can even withstand an adult.
A resident of Krasnogorsk near Moscow, who built a garden with a swimming pool on the roof of an apartment building, found followers. Not so long ago, the regional State Housing Inspectorate issued an order for the demolition of another masterpiece of building thought - this time in Khimki, where a citizen built a glazed terrace on the roof with a personal exit from the apartment.
And although he demolished his building on demand, a fine for unauthorized redevelopment it didn't cancel. “Craving for beauty at the expense of neighbors, in fact, is a self-seizure of the common property of the owners. And this not only infringes on the interests of other residents, but also leads to the destruction of the structures of the house,” Vadim Sokov, chief state housing inspector of the Moscow Region, explained the preventive measures.
Chinese Rooftop Cottages: Feel like a farmer in the city center. A photo: REUTERS
"RG" asked the question: are there legal ways to turn the roof into a place of rest for yourself and your neighbors?
Remember everyone by name
Yes, according to the State Housing Inspection. If you wish, you can set up a flower garden on the roof of an apartment building, build the same pool, put sun loungers near it so that you can sunbathe, create a gym and even open a cafe. Only the roof must first be transferred to the category of exploited, that is, it is necessary to legally stipulate the permission to go upstairs to all residents. Until this is done, only employees of offices and organizations serving the housing stock, whose property is installed upstairs, have the right to access the roof according to the decision of the State Construction Committee. Therefore, all exits are locked, the keys to which were distributed to officials. To whom exactly is usually written on the hatch that leads to the roof.
To legalize the roof, it is necessary to convene a general meeting of residents on the issue of its transfer to the ownership of the house and subsequent reconstruction. All apartment owners must vote "for" - the rule of two-thirds of the votes required for a positive decision does not apply here. With the protocol, which reflects the absolute consent of all neighbors, you can go to Rosreestr, where the roof is recognized as the property of the house, and to the housing design institute, where a reconstruction project will be prepared. Then the finished project must be coordinated with representatives of building supervision and the local authorities of the municipality on whose territory your house is located. And only after that you can start the reconstruction, being sure that no one will demolish your garden with a pool, a terrace or a golf course on the roof.

"Venice" over the shopping center in London: rest between shopping. A photo: AP
The mood of discord
The procedure seems to be simple, but for some reason, RG journalists could not find legitimate examples of the non-trivial use of the roofs of apartment buildings in the Moscow region. In the Moscow region, according to the State Housing Inspectorate, they do not exist in principle. There are several rooftop cafes already operating in Moscow, and there are rooftop projects underway. But all of them have nothing to do with housing. Cafes are located on the roofs of non-residential buildings, and for example, a recreation area with green spaces, benches and footpaths is being created on the roof of the CSKA metro station under construction.
Three years ago, there was another project of developers building a prestigious residential complex on Karamyshevskaya embankment. They announced that a real garden with benches, cafes and a playground would be laid out on the roof of the new buildings. To do this, in the construction project, it was supposed to "build up" between the apartments on the top floors and the garden another almost full-fledged floor, consisting of waterproofing, geotextiles, gravel and soil. A thousand squares of green spaces at those prices cost the developer 15 million rubles. But then another crisis struck, and the builders had no time for roof gardens - they would have to rent out apartments! The project has not yet been implemented, although it has passed all the approvals and even received an award at one of the prestigious architectural competitions.
But if we are not talking about projects, but about the possible reconstruction of the roofs of existing houses, then problems for enthusiasts begin even at the first meeting of owners. “The residents of the upper floors are usually opposed, who are afraid that the roof may leak during work. Representatives of managing organizations responsible for the repair and anti-terrorist protection of the house will take a similar position,” Vadim Sokov is sure. You can understand the management companies, for them the fewer people go to the roof, the better - less repairs will have to be done. And although formally the word of the Criminal Code in the minutes of the meeting, where only the owners vote, is not taken into account, the managers will carry out explanatory work among the residents, you can be sure.

The football field on the roof of a skyscraper in Tokyo is open around the clock. A photo: wikipedia.org
At whose expense is the banquet?
The head of the State Housing Inspectorate near Moscow and himself is not a big supporter of roof pools, which were not provided for in the original project for building a house. "As a builder by education, I can say that the transfer of the roof to the category of exploited may violate the technical characteristics of the floors," - says Sokov. However, during the reconstruction, everything can be strengthened and even shifted anew - if only there was money! But money is the second big brake in the development of the roofs of apartment buildings.
In 2013, one square meter of an exploited roof at the stage of building a house cost an average of 20 thousand rubles, told RG in a company that planned to set up a garden on Karamyshevskaya embankment. And the reconstruction process, when all the new infrastructure would have to be built into existing structures, almost doubled the price. Now, according to experts, you can safely throw 15 percent on this price tag. The roof in this situation turns out to be golden. But then you still need to maintain everything - that is, regularly pay the costs of caring for the lawn, swimming pool, mini-golf course and other property created on the roof.
But the law does not prohibit upgrading not the entire roof, but only a few square meters, which are necessary, for example, for a small terrace with a winter garden. Which then will not be maintained by all the tenants, but by a specific person who decides that without a terrace with flowers, life is not sweet to him. However, the willingness of a particular owner to pay for the project, reconstruction and maintenance of even two square meters of roof over his apartment does not negate the consent of all tenants without exception.
And how are they?
But abroad, the roofs of buildings have long been learned to be used to the delight of people.

By the way
If at least one link in the roof legalization chain is broken, the owner will be obliged to demolish any building. At my own expense. If it was not possible to call the tenant to responsibility - for example, due to his prolonged absence from the apartment, the management company will work as a "bulldozer", which will then recover all the costs from the culprit through the court. And the owner will also be fined for unauthorized seizure of the roof and its damage, which is inevitable in the process of building anything.
It is customary in our country to strictly close the roofs for visitors and consider everyone who made their way there a bully. In extreme cases, the rooftop can accommodate an observation deck, a dovecote, or a "plantation" of satellite dishes. Meanwhile, in the rest of the world, roofs are being successfully exploited for the benefit of building residents and employees, businessmen and tourists. We will talk about twenty of the most unusual examples of the use of roofs, collected from around the planet.roof garden
The most popular way to use the roof is to set up a small garden on it, where people could go to relax, admiring the city panoramas spread around and the green vegetation planted right there. Similar facilities can be found all over the world, but the largest rooftop garden is located at the top of the Marina Bay Sands hotel in Singapore, where a huge palm grove opens into a pool at the very edge of a two-hundred-meter cliff.
Rooftop pool

By the way, swimming pools are a completely different story. They are generally a very popular object for placement on the roofs of multi-storey buildings. People are not averse to swimming in them, while having a gorgeous view of the city streets and neighboring skyscrapers. At the same time, such structures appear not only in the middle of densely built-up cities, where there is no other way to equip a pool, but also in the private sector, in houses whose owners are not afraid of architectural experiments with their homes.
Rooftop restaurant

If you are no longer surprised by gourmet dishes and original interiors of restaurants, then for fresh gastronomic experiences during your upcoming vacation, you can visit restaurants located at high altitude. The tallest restaurant in the world is located in the UAE. It is called "At.mosphere" and is located on the 122nd floor (which is about 495 meters above the ground) in the Burj Khalifa, or Burj Dubai. As conceived by the creators of this institution, the restaurant was to become a real "yacht in the sky" of the highest class, the level of comfort and quality of service in which is not lower than on huge prestigious sea liners - only the landscape outside the window is not sea, but heavenly.
Football field on the roof

In Tokyo, the roofs of buildings in the city center are trying to make public space, which is so lacking on the streets of the metropolis. For example, a football field appeared at the top of one of the buildings in the Japanese capital a few years ago. Thanks to the artificial lighting system, this rooftop sports facility is open around the clock. In Tokyo, at any time of the day or night, there are many who want to kick the ball - the love for football in Japan is huge.
Tennis court in the clouds

The highest tennis court in the world, hovering over 1,000 feet above the ocean, can be found at the luxurious five-star Jumeirah Hotel in Dubai. Between tennis matches, the court is used as a helicopter landing pad. By the way, in addition to the tennis court, on the roof of the highest hotel in the world (321 m) there are swimming pools and beautiful gardens. A super-modern building in the form of a sail was erected in the sea, 280 meters from the shore on an artificial island.
"Venetian Canal" on the roof

Do you want to go boating and admire the scenery of the metropolis at the same time? Not a problem! In central London, on the roof of the Selfridges shopping center, there is another body of water that has nothing to do with the swimming pool. There is a network of canals along which you can travel in small boats designed for two people. This channel encircles the roof of the building, and its total length is 200 meters with a width of 2 meters. The Crystal Cafe is also located here - a catering establishment where you can wait for your turn to go boating.
Rainbow over the city

On the roof of one of the tallest buildings in the Danish city of Aarhus, for several years now, there has been an unusual design in the form of a rainbow circle, completely encircling the top point of this structure. The installation was created by the famous Danish-Icelandic artist Olafur Eliasson, who is known throughout the world for his experiments with light, color and space. In particular, in this case, he wanted to create a new spatial landmark for Aarhus, in which colors are important, not cardinal points. So the inhabitants of the city no longer live in the northern or southern part of it, but in red, purple or yellow, depending on the direction of the colors of the rainbow in this installation.
Installation "Cloud City"

It would be strange if one of the world's largest venues for contemporary art, the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York, did not try to use the building's roof for its own needs. There is a large-scale installation called "Cloud City" by architect Tomas Saraceno. It is a multi-storey structure of complex shapes connected by metal joints and steel cables. Inside this object, you can walk, thus discovering the geometry of New York from a new perspective.
Open air cinema

England never ceases to amaze: a cinema on the roof of the house has recently opened in London! Three friends decided to open their own video room for friends and family on the roof of their own house. Having collected the necessary papers from the government, confirming the non-commercial component of the idea itself, the British built an excellent open-air cinema overlooking London. At first they just watched their favorite movie with popcorn, and now on the roof instead of chairs there are inflatable pools for several people! A movie show, so to speak, without departing from the "jacuzzi" ... By the way, the rooftop cinema "Rooftop Cinema", which can accommodate up to 500 people, is also in Tallinn.
Roof top amusement park

Let's finish the first part of our review with dizzying entertainment. Did you know that on the roof of the Stratosphere skyscraper in Las Vegas there is an amusement park for people who are not afraid of heights? Whirling on a carousel and other attractions, visitors to this park will, indeed, practically in the "stratosphere" - at an altitude of 250 meters above ground level. Would you have the courage?
I tried to collect all the stadiums in the world with a closing roof. Some of them were mentioned earlier, and even were described in detail in previous materials. Each of these stadiums is interesting in its own way and deserves a separate story, but in this case it is just a selection, so to speak, without unnecessary details.
Taking into account those being designed and under construction, it turned out 44 stadiums.
ESPRIT arena(ESPRIT arena), Düsseldorf, Germany. Capacity 54 500, built in 2004. Home stadium of FC "Fortuna".

Commerzbank Arena(Commerzbank-Arena), Frankfurt am Main, Germany. Capacity 52,300, built in 2005. Eintracht's home stadium.

Turk Telekom Arena(Turk Telekom Arena), Istanbul, Turkey. Capacity 52,650, built in 2011. Galatasaray Stadium.

Under construction stadium in St. Petersburg. Probable name Gazprom Arena. Capacity 69,000. Will have an outgoing field. Future stadium "Zenith".

Gelred(Gelredome), Arnhem, Holland. Capacity 29 600, year of construction 1998. Has an exit field. Home stadium of the club "Vitesse".

Feltins Arena(Veltins-Arena), Gelsenkirchen, Germany. Capacity 61 482, year of construction 2001. Has an exit field. Home stadium "Schalke 04".

University of Phoenix Stadium(University of Phoenix Stadium), a suburb of Phoenix, Glendale, Arizona, USA. Capacity 63 400, year of construction 2006. Has an exit field. Home stadium of the Arizona Cardinals.

Cowboys Stadium(Cowboys Stadium), a suburb of Dallas, Arlington, Texas, USA. Capacity 91,600, built 2009. Dallas Cowboys stadium.

Relint Stadium(Reliant Stadium), Houston, Texas, USA. Capacity 71,500, year built 2002. Home stadium of the Houston Texans.

Lucas Oil Stadium(Lucas Oil Stadium), Indianapolis, Indiana, USA. Capacity 70,000, year of construction 2008. Home stadium of the Indianapolissolts club.

Stadium under construction Shwedbank Arena(Swedbank Arena), Stockholm, Sweden. Capacity 50,000. The future stadium of the AIK club and the Swedish national team.

People's Stadium(Stadion Narodowy), Warsaw, Poland. Capacity 58,145, year of construction 2011. Poland national team stadium.

National Arena(National Arena), Bucharest. Capacity 55,600, built in 2011. Home stadium of the Romanian national team.

Wembley(Wembley), London, England. Capacity 90,000, built 2007. England stadium. On it, the roof is closed, but not over the field, but over the stands - on both sides behind the goal and a small fragment above the central stand.

Rogers Center(Rogers Centre), Toronto, Canada. Capacity 54,000, built in 1989. The world's first stadium with a fully closed roof. Home stadium of the Toronto Argonauts.

Big Eye Stadium(Stadium Big Eye), Oita, Japan. Capacity 43,000, built in 2001. Became the first stadium in the world of the Olympic format with a closing roof. Home stadium of FC Oita Trinita.

Nantong Stadium(Nantong Stadium), Nantong, China. Built in 2010 according to the design of the stadium in Oita. Capacity 32,244.

Kobe Wing Stadium(Kobe Wing Stadium), Kobe, Japan. Built in 2001, capacity 30,132. Home stadium of FC Vissel Kobe.

Kazhymukan Stadium, Astana, Kazakhstan. Capacity 30,000, year of construction 2009. Stadium of FC Lokomotiv Astana.

Etihad Stadium(Etihad Stadium), Melbourne, Australia. Capacity 56,000, built in 2000. Home stadium of the Melbourne Victory club.

Millennium(Millennium), Cardiff, Wales. Capacity 74,500, built 1999. Home of the Wales national team.

Amsterdam Arena(Amsterdam ArenA), Amsterdam, Holland. Capacity 51,628, year built 1996. Ajax's home arena.

Chase Field(Chase Field), Phoenix, Arizona, USA. Although the stadium is a baseball stadium, it is still a stadium. Capacity 49,000, year of construction 1998. Home arena of the Arizona Diamondbacks club.

Fukuoka Dome(Fukuoka Dome), Fukuoka, Japan. Also baseball. Capacity 35,695, built 1993. Home stadium of the Fukuoka Hawks.

Safeco Field(Safeco Field), Settle, Washington, USA. With a football configuration of the field, the capacity is 30,144, built in 1999. Home stadium of the Seattle Mariners club. When open, the roof creates a canopy near the stadium.

Project Vikings Stadium(Vikings Stadium), Minneapolis, Minnesota, USA. Estimated capacity is 73,000. The future stadium of the Minnesota Vikings club.
rugby project Arenas 92(Arena 92), Paris, France. Capacity 32,000. The future stadium of the Racing Metro 92 club.

Reconstruction project Marseille Picot Stadium(Stade Marcel-Picot), a suburb of Nancy, Tomblaine, France. Capacity is now 20,087, according to the project 33,000. Home stadium of the Nancy club.

Under construction Le Grand Stade(Le Grand Stade), Lille, France. Capacity 50 186. Lille Stadium.

Miller Park(Miller Park), Milwaukee, Wisconsin, USA. Capacity 41,900, built 2001. Home stadium of the Milwaukee Brewers.

Minute Maid Park(Minute Maid Park), Houston, Texas, USA. Another baseball stadium. Capacity 40,950, year built 2000. Home to the Houston Astros.

parken(Parken), Copenhagen, Denmark. Capacity 40,000, built in 1992. Recently renovated. The home stadium of the Danish national team and FC Copenhagen.

BBC Place(BC Place), Vancouver, Canada. Capacity 59,841, built in 1983, renovated in 2011.

Toyota Stadium(Toyota Stadium), Toyota, Japan. Capacity 45,000, built in 2001. Did not host World Cup 2002 matches. The architect of the stadium is Kise Kurokawa (the one who designed the St. Petersburg stadium). The home stadium of the Nagoya Grampus.
 Under construction Merlins Ballpark(Marlins Ballpark), Miami, Florida, USA. Capacity 37,000.
Under construction Merlins Ballpark(Marlins Ballpark), Miami, Florida, USA. Capacity 37,000. 
Stadium under construction Stockholmsarenan(Stockholmsarenan), Stockholm, Sweden. Capacity 30,000.

Closing roof project Sukru Saracoglu(Sukru Saracoglu), Istanbul, Turkey. Fenerbahce Stadium.

Under construction Sports Hub Stadium(Sports Hub Stadium) in Singapore. The capacity will be 55,000.

stadium project Farmers Field(Farmers Field), Los Angeles, California, USA. The capacity will be 76,000.

The project of the new stadium of the club De Graafschap, Doetinchem, Holland. Future capacity 20,396.

Ordos Stadium(Ordos Stadium), Ordos, China. Built in 2011 for $151 million. Capacity 45,076.

Lazio stadium project Stadio delle Aquile(Stadio delle Aquile), Rome, Italy. Future capacity 55,000.

Stadium project in Kaliningrad for the 2018 World Cup. Future capacity is 45,015, reduced to 25,000.

Project Sports City Stadium(Sports City Stadium) in Qatar for the 2022 World Cup. The capacity will be 47,560.
Photos taken from stadiums.at.ua
P.S. Subscribe to the blog!
P.S. Appreciate the post!
| Information about the conditions for obtaining documentation is available only to registered users, authorization is required | |
          |
|
A football field measuring 90 m x 60 m playing area is designed above the underground car park. The football field includes stands for spectators for 100 seats, with accommodation for 3 seats for wheelchair users. The football field surface is a permeable polyethylene artificial grass backfilled with quartz sand and equipped with a drainage system.
Main technical indicators: area of the land plot within the boundaries of the design 14,174 sq.m.; building area including football field 7,390 sq.m.; football field area 6,290 sq.m.; total area 7 157 sq.m.; construction volume 24,755 cubic meters; number of parking places - 177 cars; throughput capacity of the football field 22 people/cm; the capacity of the stands is 100 people. The estimated cost of construction is 335.2 million rubles.
Documentation in DWG, DOC, XLS format. The composition of the documentation:
Section 1 - code-PZ - Explanatory note
Section 2 - code-ROM - Scheme of the planning organization of the land plot
Section 3 - cipher-AR - Architectural solutions
Section 4 - code-KR - Structural solutions
Section 5 Information about engineering equipment, engineering and technical support networks, a list of engineering and technical measures, the content of technological solutions
Section 5.1 - code-IOS1 - Power supply system
Section 5.2 - code-IOS2 - Water supply and sanitation systems
Section 5.3 - code-IOS3 - Water supply and sanitation systems. Outdoor networks
Section 5.4.1 - code-IOS4.1 - Ventilation and air conditioning
Section 5.4.2 - code-IOS4.2 - Heating
Section 5.4.3 - code-IOS4.3 - Individual heat point
Section 5.4.4 - code-IOS4.4 - Heat networks
Section 5.5.1 - code-IOS5.1 - Communication networks
Section 5.5.2 - code-IOS5.2 - External communication networks
Section 5.5.3 - code-IOS5.3 - Communication networks. Automation of engineering systems
Section 5.6 - code-IOS5.6 - Technological solutions
Section 5.7 - code-IOS5.7 - Automatic fire extinguishing system
Section 6 - cipher-POS - Construction organization project
Section 8 - code-OOS - List of measures for environmental protection.
Section 9 - code-PB - Measures to ensure fire safety.
Section 10 - cipher-ODI - Measures to ensure access for persons with disabilities
Section 10.1 - code-EE - Measures to ensure compliance with energy efficiency requirements and the requirements for equipping buildings, structures and structures with metering devices for energy resources used
Section 11 - code-SM - Estimate for the construction of capital construction projects
Description of technological solutions. The project provides for the placement on the site of several volumes for various purposes:
Underground car park
Parking for 177 cars is designed at el. -3.750 with two attached single-track rectilinear unheated ramps, isolated from the car park with overhead sectional doors 4.5 m wide with wickets.
The placement of vehicles with engines running on compressed natural gas is not provided.
Parking in the places of car storage is equipped with wheel breakers. The planned underground car park is heated.
At the ramp used for entry, a security room was designed,
which is equipped with a dignity. node. There is a window in the security room,
designed to monitor the entry of vehicles into the underground parking. The project provides a place for storing cleaning equipment in the parking lot.
Engineering and technical premises were designed as part of the parking lot: two ventilation chambers, a fire extinguishing pump room, an ITP room, and electrical panel rooms.
The parking lot is open 24/7 in one shift (24 hours a day).
The number of people working in the garage in the maximum shift is 1 person.
Football stadium
The stadium is intended for mass independent and organized sports and recreation and sports and leisure activities for all categories of the population living in the area. The size of the playing field is 90.0 x 60.0 m. The playing field is designed above the underground car park and can be used for playing bast shoes, football, field hockey. The stadium has been designed with stands for 100 spectators, as well as 3 places for wheelchair users. The tribunes are designed to be stationary, based on a metal frame, individual plastic seats for the stationary stands of Luzhniki (corresponding to accepted international standards for strength, combustibility and temperature operation) are used as seats for spectators.
The entrance of spectators to the stadium is designed from the side of residential buildings through the passage between the amenity and auxiliary premises.
The stadium is designed with:
- a playing field common to all involved;
- locker rooms for those involved;
- rooms for trainers;
- storage facilities for sports equipment;
- Technical buildings.
The main and auxiliary premises of the stadium are designed in accordance with the main technological indicators:
a) throughput of the stadium during the competition:
- involved - 22 people / shift;
- spectators - 100 people;
- number of shifts - 3;
- shift duration - 2.0 hours;
b) throughput capacity of the center during training sessions:
- involved in the stadium - 32 people / shift;
- number of shifts - 6;
- Duration of one shift - 2 hours.
c) the maximum number of coaches is 4 people (simultaneously working at the stadium - 2 people).
The capacity of the field during training sessions according to SP 31-115-2006 is 32 people. Designed two team locker rooms for 16 changing places each. All dressing rooms are equipped with two-section lockers for storing home clothes, interlocked with changing areas. The number of lockers - 48 pieces - is accepted in accordance with the operating experience at 150% of the throughput of the playing field per shift.
Showers and sanitary facilities are provided directly communicating with the dressing rooms. Hair dryers are installed at the rate of 1 hair dryer per 10 people.
In the locker rooms, the project provides for two coaching rooms. In the coaching rooms there are two-section lockers for storing clothes for 2 people, interlocked with places for changing clothes, a workplace for keeping records and a recreation area.
For the storage of sports equipment, an inventory room is provided for the placement of portable sports equipment.
An ambulance is expected to be on duty at the stadium to provide emergency care in case of injuries and conduct medical monitoring of athletes during mass competitions at the stadium.
Two bathrooms are designed for visitors. node (male and female) and a separate dignity. a node for people with limited mobility, as well as a room for storing cleaning equipment.
- Platform for seasonal trading
On the exploited roof, the project provides for an open area at elevation +3.500 for seasonal trade, rectangular in plan with dimensions of 7.70 m x 46.40 m.
For sellers and visitors, a metal staircase was designed from the side of the main facade in the N-L axes.
For transportation of goods to the trading floor, a cargo lift is provided from the level of the loading platform to elev. plus 0.100 to the level of the unloading platform at elevation +3.500 and an additional evacuation open ladder. The site is protected from precipitation by a polycarbonate canopy in metal structures.
There is a 1.5 m high fence along the perimeter of the site.
- Car wash
As part of the auxiliary premises of the ground part, a car wash is provided, which has two posts for manual washing of cars.
In order to save fresh water, the project provides for a car wash recycling water supply system, which is equipped with its own treatment facilities of the Moydodyr-M-KF-3 model of CJSC Concern Moidodyr, Moscow, with a capacity of 2.2 cubic meters per hour. Dirty water from car washing are collected in a tray in the floor of the washing compartment and enter the receiving tank, where large particles of dirt settle.To retain the largest fraction of suspended solids, transverse partitions are installed in the trays.
Treatment facilities for car washes of the Moidodyr-M series consist of a hydrocyclone, a thin-layer shelf sedimentation tank, a floating load filter, a coagulant dosing system and a control unit. This treatment plant is equipped with an oil separator, a flotation tank, a coagulant dosing system and an automatic chlorine dosing device for car washes. The concentration of contaminants in the outlet water: for suspended particles - no more than 20 mg / l, for oil products - no more than 10 mg / l. The installation works in automatic mode. To make up for water losses during operation, a connection to the water supply network is provided.
Manual washing stations are equipped with high-pressure apparatus manufactured by "KARCHER" (Germany). The capacity of the posts is approximately 4 cars per hour. The washing cycle includes: washing with a high-pressure apparatus with a dosing supply of a special shampoo; rinsing with water using a high-pressure apparatus; drying and cleaning the interior with the help of vacuum garbage collectors, water and dirt model NT561Eco. After washing, the car is handed over to the customer.
Supply and exhaust ventilation is designed in the car wash room. To remove exhaust gases from the high-pressure apparatus, two exhaust coils with a flexible hose and a mechanical drive for wall mounting are provided with a capacity of 350-500 cubic meters / hour and an air flow rate in the hose of 10-15 m / s, which completely eliminates the possibility of exhaust gases entering the room.
The operating mode of the washing area is round-the-clock in 3 shifts (8 hours each).
The number of people working at the sink in the maximum shift is 4 people.