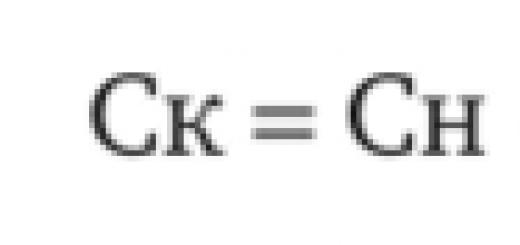Remote banking
| This article lacks links to sources of information.
Information must be verifiable, otherwise it may be questioned and removed. |
Remote banking service (RBS)- a general term for technologies for providing banking services based on orders transmitted by the client remotely (that is, without his visit to the bank), most often using computer and telephone networks. To describe remote banking technologies, various terms that in some cases overlap in meaning are used: Client-Bank, Bank-Client, Internet Bank, Remote Banking System, Electronic Banking, Internet Banking, on-line banking, remote banking, direct banking, home banking, internet banking, PC banking, phone banking, mobile banking, WAP banking, SMS banking, GSM banking, TV banking.
Types of remote banking services (RBS)
RBS technologies can be classified according to the types of information systems (software and hardware) used for banking operations:
Client-Bank systems (PC-banking, remote banking, direct banking, home banking)
Systems accessed through a personal computer. The Bank at the same time provides the client with technical and methodological support during the installation of the system, initial training of the client's personnel, software updates and support of the client in the process of further work. Client-Bank systems provide full-fledged settlement and depositary services and maintenance of ruble and foreign currency accounts from a remote workplace. Client-Bank systems allow you to create and send payment documents of any type to the bank, as well as receive account statements from the bank (information about movements on the account). For security purposes, the Client-Bank systems use various encryption systems. The use of Client-Bank systems for servicing legal entities is still one of the most popular RBS technologies in Russia. Client-Bank systems are fundamentally divided into 2 types (thick client and thin client):
Bank-Client (fat client)
The classic type of the Bank-Client system. A separate client program is installed on the user's workstation. The client program stores all its data on the computer, as a rule, these are payment documents and account statements. The client program can connect to the bank via various communication channels. Most often, a direct connection or via the Internet is used to connect to the bank.
Internet Client (thin client) (On-line banking, Internet banking (Internet banking), WEB-banking)
The user logs in through an Internet browser. The Internet Client system is hosted on the bank's web server. All user data (payment documents and account statements) are available on the bank's website. Using the Internet Client technology, systems for mobile devices are also built (mobile website of the bank) - PDA, smartphones (Mobile banking (mobile-banking). Based on the Internet Client, information services with a limited set of functions can be provided.
Remote banking via the Internet has a number of both advantages and disadvantages. Thus, the advantages for organizations providing such services include the low cost of operating an Internet system (all updates are carried out only on a web server, not replicated by customers); the ability to integrate with the client's accounting systems; availability of Internet services for the end user; maintaining the loyalty of customers who actively use these services.
The disadvantages include, first of all, the weak security of the Internet from unauthorized access. Despite the desire of Internet solution developers to create and improve the system for protecting transmitted messages, numerous potential dangers continue to appear. Reasons: shortcomings of operating systems, communication programs and browsers, human factor. Maintaining the level of protection at an appropriate level requires significant material costs, which can be afforded mainly by large banks, which rely on significant income from the provision of such services.
Phone-Bank systems (Telephone banking (phone-banking), telebanking, Phone-Client, SMS-banking)
As a rule, Phone-Bank systems have a limited set of functions compared to Client-Bank systems:
- information about account balances;
- information on the amount of receipts in favor of the client;
- entering applications for the provision of a facsimile copy of the account statement;
- entering applications for making payments, ordering cash;
- entering applications for the transfer of a facsimile copy of a payment order;
- entering an application for the execution of an instruction prepared according to the template for the transfer of funds;
The transfer of information from the client to the bank can be done in various ways, depending on the implementation of the system:
- Communication of the client with the operator of telephone service (Call Center).
- Using a push-button telephone (Touch Tone Telephone) and a voice menu (computerized telephone communications (IVR (Interactive Voice Response) technologies), Speech to Text, Text to Speech).
- By sending SMS messages (SMS-banking)
All these functions become available only after the personal identification of the client by the bank based on the personal identification system. To date, the most advanced and secure system is based on biometric identification cards.
Service using ATMs (ATM-banking) and self-service banking devices
RBS technologies using self-service banking devices are among the most popular in the world and in Russia. There are several types of RBS according to the type of devices used:
- RBS using ATMs (ATM-banking) - based on software installed on bank ATMs. See also Bank card
- RBS using payment terminals;
- RBS using information kiosks.
financial regulation
RBS services are regulated by the following provisions of the Central Bank of Russia:
- Regulation No. 302-P dated March 26, 2007 “On the Rules for Maintaining Accounting in Credit Institutions Located in the Territory of the Russian Federation”
- Regulation No. 2-P dated 03.10.2002 “On non-cash payments in the Russian Federation”.
- Regulations No. 318-P dated April 24, 2008 “On the procedure for conducting cash transactions in credit institutions in the Russian Federation” (clause 2.8 “Organization of work with cash when using ATMs, electronic cashiers, automatic safes and other software and hardware complexes” );
- Regulations No. 36-P dated June 23, 1998 “On Interregional Electronic Settlements Through the Settlement Network of the Bank of Russia”;
- Regulations No. 20-P, dated March 12, 1998, “On the Rules for the Exchange of Electronic Documents between the Bank of Russia, Credit Institutions (Branches) and Other Clients of the Bank of Russia When Making Settlements Through the Settlement Network of the Bank of Russia”.
- Temporary Regulation No. 17-P dated February 10, 1998 “On the Procedure for Accepting for Execution Orders of Account Holders Signed with Analogues of a Handwritten Signature when Conducting Cashless Payments by Credit Institutions”
In addition, the following requirements must be taken into account:
- Federal Law No. 63-FZ of April 6, 2011 “On Electronic Signature”;
- Standard of the Bank of Russia STO BR IBBS-1.0-2006 "Ensuring information security of organizations of the banking system of the Russian Federation;
- Bank of Russia Letter No. 16-T dated April 3, 2004 “On Recommendations on the Information Content and Organization of Credit Institutions' Websites on the Internet” (instead of it No. 128-T dated October 23, 2009);
- Bank of Russia Letter No. 115-T, dated August 30, 2006, “On the Implementation of the Federal Law “On Combating the Legalization (Laundering) of Proceeds from Crime and the Financing of Terrorism with regard to the Identification of Clients Serviced Using Remote Banking Technologies (including Internet Banking)” »;
- Bank of Russia Letter No. 60-T, dated April 27, 2007, “On the Peculiarities of Servicing Clients by Credit Institutions Using the Technology of Remote Access to a Client’s Bank Account (Including Internet Banking)”;
- Bank of Russia Letter No. 197-T dated 07.12.2007 “On Risks in Remote Banking Services”;
- Bank of Russia Letter No. 36-T, dated March 31, 2008, “On Recommendations for Organizing the Management of Risks Arising from Credit Institutions Conducting Transactions Using Internet Banking Systems”;
- Letters of the Bank of Russia No. 11-T dated January 30, 2009 “On recommendations for credit institutions on additional information security measures when using Internet banking systems”
- Bank of Russia Letter No. 141-T, dated October 26, 2010, “On Recommendations on the Approaches of Credit Institutions to the Selection of Providers and Interaction with Them when Providing Remote Banking Services”
RBS services are regulated by the following provisions of the National Bank of Ukraine:
- Instruction No. 22 of January 21, 2004 on non-cash payments in Ukraine in the national currency, Chapter 11.
Work in the system is a session exchange of documents initiated by the client.
The client can perform the following operations through the bank:
A complete list of documents involved in the exchange between the client and the bank can be found in the Terms of Remote Banking Services.
Tariff determines what commissions are charged by the Bank for the provision of services to the Client.
The list of services for which a fee is charged is suggested in the table below.
The full list of tariffs can be found on the page.
The tariff and the corresponding commission sizes must be specified on the its regional branch or in the branch of the Bank.
|
Name of service |
Note |
|
|
Installing and configuring software, restoring the current operability of the remote banking system with a visit to the client |
||
|
By regional branch |
The commission is charged on the day of submission to the Bank of the Application signed by the client for the performance of work related to the installation and configuration of software and means of cryptographic protection of information of the client module of the RB system. |
|
|
Transferring a client to a new RBS system |
||
|
Transfer of a client from the RBS system "Bank-Client" to the RBS system "Internet-Client" (at the request of the client) |
The commission is charged on the day the client submits an application to the Bank. Transfer of a client to another RBS system is carried out within 15 working days from the moment the client submits an application |
|
|
Transfer of the client to a new version of the RBS system with the provision of software and key media containing signature key certificates issued to specially authorized persons of the client. |
For customers who have previously concluded a Customer Service Agreement with the Bank using documents in electronic form signed with an electronic digital signature |
|
|
RBS system maintenance |
||
|
"Bank-Client" |
The commission is charged monthly no earlier than the 25th day and no later than the last working day of the current calendar month, starting from the month following the month of the client's connection to the Bank-Client RBS system. The commission is charged from the client, regardless of the number of accounts of this client connected to the Bank-Client RBS system. When transferring a client from one RBS system to another in accordance with clause 7.2.1, a new fee is charged from the month following the month of connection to the new RBS system. In case of termination of the agreement on the provision of remote banking services during the billing month, the commission is charged in proportion to the number of working days of using the service in this month. According to p.p. 7.3.2-7.3.3 the service is provided to clients who have previously concluded a Client Service Agreement with the Bank using documents in electronic form signed with an electronic digital signature, until the client is transferred to a new version of the RB system. When a client uses the Bank's services under paragraphs. 7.3.2-7.3.3 the commission under clause 7.3.1 is not charged by the Bank |
|
|
When connecting more than one client to one automated workstation of the Bank-Client RBS system |
||
|
When one client installs several automated workstations of the Bank-Client RBS system |
||
|
Maintenance of cryptographic information protection |
||
|
Making one temporary |
The commission is charged on the day the client submits an application for registration of the client at the Certification Center of Rosselkhozbank JSC. The tariff includes VAT (additionally not charged) |
|
|
The service is provided to the client after fulfilling the conditions under clause 7.4.1 |
||
|
Cancellation (revocation) of the signature key certificate at the request of the client |
||
|
Suspension of a single signing key certificate at the request of a client |
||
|
Renewal of the validity of one signing key certificate at the request of the client |
The commission is charged within 3 working days from the date of renewal of the signature key certificate for the Information Exchange Subject. The tariff includes VAT (additionally not charged) |
|
|
Authentication of the electronic signature (ES) in one electronic document at the request of the client |
The commission is charged within 3 working days from the date of the conclusion of the Certification Center of Rosselkhozbank JSC. The tariff includes VAT (additionally not charged) |
|
|
Scheduled change of the signature key certificate at the request of the client |
||
|
Making a signing key certificate |
||
|
Unscheduled change of the signing key certificate at the request of the client |
||
|
Production of one temporary signature key certificate on a new key carrier due to the loss of the key carrier or its technical damage |
The fee is charged on the day the client submits a request to revoke/suspend the signature key certificate. The tariff includes VAT (additionally not charged) |
|
|
Production of a signature key certificate at the request of the client |
The service is provided to the client after fulfilling the conditions under clause 7.6.1 |
|
|
Production of a temporary signature key certificate in connection with the compromise of the signature key on a new key carrier |
The tariff is applied in case the client returns the key carrier previously issued by the Bank. If the client fails to provide a key carrier previously issued by the Bank, the client is charged a fee in accordance with clause 6.1 on the day the client receives a new key carrier from the Bank |
|
|
Production of a signature key certificate at the request of the client |
The service is provided to the client after the conditions under clause 7.6.2 are met |
|
Before drawing up documents for connection, you must familiarize yourself with the Terms of Remote Banking Service with appendices and.
Connection to the system is carried out in three visits to the bank.
First visit
It is necessary to submit at the bank office:
1. Application for accession to the Terms of Online Banking
Fill example
2. Application for registration in the Certification Center of Rosselkhozbank JSC (one application for each authorized person of the client specified in the Application for accession to the Terms of Remote Banking Services)
Fill example
Second visit
1. Obtaining a separate FKN for each specified authorized person of the client. The FKN is a key carrier on which a temporary key for verifying an electronic signature is recorded.
2. Using FKN with temporary keys, you need to connect to the system at your workplace and create permanent keys 1 . After that, for each authorized person, you need to create and print Request for the issuance of a certificate of the electronic signature verification key, which is available electronically in the system.
Instructions: First login and permanent key generation
Third visit
1. Transfer of completed Requests for the issuance of a certificate of the electronic signature verification key to the bank.
2. The bank issues the requested certificates in electronic form, after receiving them and recording them on the FKN, you can start fully functional work in the system.
Important!
- All documents are submitted to the bank in duplicate.
- A request for issuing a certificate of an electronic signature verification key must be created no later than 45 days from the date of issue of temporary keys.
1 Working with the RBS CA in terms of receiving statements, sending payments and other operations is possible only with permanent verification keys.
Hardware requirements:
IBM-compatible computer with a Pentium II class processor, 400 MHz or higher;
the amount of RAM is not less than 512 MB;
free disk space of at least 500 MB;
the presence of a CD-ROM;
free USB port;
information output means (display/monitor) with a resolution of at least 800*600;
connection to the Internet to communicate with the Bank;
the presence of a connected local or network printer;
System Software Requirements:
32/64-bit operating system of the Microsoft Windows Vista family, Microsoft Windows 7, Microsoft Windows 8.1, Microsoft Windows 10 in which it is recommended to set the following password policy settings: the minimum password length is 8 characters, the system procedure for checking password complexity is activated, automatic locking of personal computer for 20 minutes after 5 unsuccessful attempts to enter a password, an automatic request to change the password is set after 3 months from the start of its use;
browser Microsoft Internet Explorer version 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10, 11.
it is necessary to ensure the absence of viruses and other malicious programs in the operating environment, as well as keeping anti-virus databases up to date using certified anti-virus software;
In case of detection of failures in the system operation, it is necessary to notify the Bank about the problem by contact phone 8-800-100-0-100 (from 09.00 to 18.00, regional branch time).
To install the Bank-Client system, the bank provides the client with an installation kit.
The installation kit of the Bank-Client system includes physical storage media:
CD containing the distribution kit of the client part of the software;
the main certificate of the electronic signature verification key and the backup certificate of the bank's electronic signature verification key;
FKN 2 with a temporary key pair and the corresponding Certificate of electronic signature verification keys for each of the Authorized Persons;
license to use CIPF "CryptoPro CSP";
documentation for working with the "Bank-Client" system and CIPF.
Installation and configuration of the software can be carried out by the client independently or carried out by the Bank on the basis of the Client's Application for installation and configuration of software for remote banking systems 3 (to the Terms of Remote Banking Services). When carrying out work on installing and configuring the system, the presence of a responsible employee of the client's accounting department and a person responsible for the client's technical means is required.
Important!
It is allowed to copy the software supplied by the bank only for the purpose of creating backup copies for system recovery.
1 CIPF is a certified means of cryptographic information protection
2 FKN - functional key carrier
3 Installation and configuration of the system is carried out in accordance with the tariffs.
Reference material on the Bank-Client system is provided to the Client in the installation kit.
The Bank provides the Rostec State Corporation entities with the Bank-Client/Internet-Client centralized banking system universal service within the framework of the Terms and Conditions for providing the Rostec State Corporation entities with the Bank-Client/Bank-Client centralized remote banking system universal service. Internet Client.
To receive the service, it is necessary to fill out the Application for accession to the Terms and submit it to the division of the Bank serving your organization.
Documents required to connect to the RBS CA:
Dear Clients!
From 10/16/2017 new functionality is available in the system of RB RB and RBSS GOZ in terms of obtaining more detailed information about the account status and documents sent to the Bank in the "on-line" mode.
During the operating day, you will be able to receive information about the available balance of funds on the account, in the presence of an overdraft - the balance, taking into account the unused overdraft limit.
www.cryptopro.ru
Information on executed payments and credited receipts of funds is available immediately after the transaction, with a delay of no more than 10 minutes (the maximum time spent on transferring information to your "Internet client").
To use this functionality in your work, we recommend that you read the brief instructions for viewing balances and statements for the current day
Dear Clients!
In accordance with paragraph 138 of the joint order of the Ministry of Telecom and Mass Communications of Russia and the Ministry of Construction of Russia dated December 28, 2015 No. 589/944 / pr, credit organizations through which payments for housing and utilities are made in favor of organizations registered in the register of suppliers are required to place in the GIS Housing and communal services a list of mandatory details that identify the payment, among which one of the unique identifiers must be present (see recommendations for filling out payment orders when paying for residential premises and utilities, the Memo for housing and communal services).
Dear Clients!
In connection with the entry into force on 28.03.16. amendments to the Order of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation of November 12, 2013 N 107n, it is necessary to be guided by this Memo on the execution of orders for the transfer of funds to the budget system of the Russian Federation when issuing orders to transfer funds to pay payments to the budget system of the Russian Federation.
The bank was registered in Moscow in September 1994. Since August 2005, it has been a member of the deposit insurance system. In February 2015, the bank changed its legal form from CJSC to JSC.
To date, the main beneficiaries of the financial institution are the founder, co-owner and president of CJSC NK Nobel Oil * Grigory Gurevich (58.33%), as well as minority shareholders of this oil company, including the wife of Grigory Gurevich Vera Artyakova (through various structures controls 37 04% of the bank's shares) and their daughter Maria Nazarova (0.23%). Igor Gorlushkin (4.40%) is also among the ultimate beneficiaries of the credit institution.
The head office of the bank is located in Moscow. The sales network also includes two additional offices in the Moscow region, 11 credit and cash offices in other Russian cities (five of them in the Republic of Crimea) and an operational office in Gus-Khrustalny. Own network of ATMs is represented by seven devices located on the territory of structural divisions. The headcount at the beginning of 2017 was 229 employees (a year earlier - 280 employees).
In addition to individuals, the bank names oil, food, processing and light industries, pharmaceuticals and medical equipment, publishing and printing industry, agro-industrial complex, information technology, construction and transport as its main clients.
Legal entities are offered the whole range of basic banking services, including settlement and cash services, provision of guarantees, placement of funds on deposits, remote services (the "Client - Bank" system), payroll projects and corporate bank cards, merchant acquiring, rental of safe deposit boxes, currency transactions, lending (including small and medium-sized businesses), as well as leasing operations.
Individuals have access to a wide range of deposits, settlement and cash services, rental of safes, payments and money transfers (Contact, UNIStream, money transfers to and from Crimea), bank cards (Visa, MasterCard), Internet banking, brokerage services. Consumer lending is currently not carried out by the bank, with the exception of lending to employees or persons recommended by the governing bodies of the financial institution. As part of a special offer, the bank also offers mortgage lending for the construction of a cottage in the Zadorino village.
Among its clients, the bank noted OOO PO Eleron, OOO Yuza, OOO Laguna, OOO Petrusko, OOO MV-Nedvizhimost, OOO Plastavia, OOO Russian Lead Group of Companies, OOO PO Eleron, LLC Service-Integrator, LLC Trade House Appolo, etc.
Since the beginning of 2017, the assets of the credit institution have increased by 7.5%, amounting to 18.5 billion rubles by August 1. In liabilities, the main increase was provided by interbank loans, the volume of which increased by 2.5 times. In assets, the attracted liquidity was directed to lending to legal entities, investments in securities and the interbank loan market. The bank also received part of the funds, reducing highly liquid balances by almost a third.
The bank is characterized by an increased concentration of the resource base on household deposits, although their share has slightly decreased since the beginning of 2017 - from 73.1% to 68.2% by the reporting date. Funds from individuals are mainly attracted for terms from one to three years. Attracted interbank loans form 13.0% of liabilities as of the reporting date (at the beginning of 2017 - 5.6%), all funds are attracted for short periods from commercial banks (in the reporting for the first half of 2017, the entire volume of interbank loans was attracted from Bank National Clearing Center” within the framework of direct REPO transactions). The share of funds of enterprises and organizations in liabilities is 8.8%: the structure is dominated by perpetual subordinated loans included in the calculation of fixed capital, deposits with a maturity of six months to a year, and current account balances. By August 1, 2017, the total adequacy of the bank's own funds fell below 11% (with a minimum of 8%) and completely coincides with the adequacy of the core capital (minimum - 6%). At the same time, the adequacy of the basic capital, which does not include perpetual subordinated loans, is almost twice as low as the total adequacy of own funds - 6.1% (with a minimum of 4.5%). A share of 0.2% of liabilities is formed by own issued promissory notes. The credit institution's client base is small, with stable payment dynamics. Turnovers on customer accounts in recent months were at the level of 6 billion rubles.
About 62% of net assets are accounted for by the loan portfolio, 14.1% form investments in securities, 9.5% - other assets (mainly represented by claims on other operations), 5.1% - highly liquid assets (cash and bank balances). correspondent accounts), 4.4% - issued by interbank loans, 5.4% - fixed assets and intangible assets.
As of August 1, 2017, the loan portfolio is RUB 11.4 billion and has shown an increase of 5.6% since the beginning of the year due to corporate lending (+0.6 billion rubles, or +6.0%). Loans to legal entities form 96.5% of the total portfolio. Retail loans on the balance sheet are represented by consumer loans, housing and car loans. Since the beginning of 2017, the bank has more than halved the amount of overdue debt (a decrease was observed in both retail and corporate portfolios), the share of overdue loans in total loans decreased over the same period from 3.0% to 1.3%. The level of provisioning is high and, in contrast to the delay, has increased significantly since the beginning of 2017 - from 7.0% to 11.3% of the loan portfolio. The level of collateral for the loan portfolio is assessed as insufficient (85.0%).
The sectoral structure of the corporate loan portfolio, according to the explanatory information to the reporting for 2016, was dominated by the following sectors of the economy: wholesale and retail trade (28.5%), manufacturing (12.8%), real estate transactions (11.2 %) and construction (5%). A significant share was also accounted for by other types of activities (27.4%).
According to IFRS statements, at the end of 2016 the bank had 22 borrowers (a year earlier - 27 borrowers) with a total amount of loans issued to each borrower in excess of 10% of the bank's equity. The total amount of these loans amounted to 7.95 billion rubles (a year earlier - 8.2 billion rubles), or 65.7% of total loans and borrowings before deduction of allowance for impairment of loans and receivables (a year earlier - 73%).
The securities portfolio - 2.6 billion rubles, has grown by 21% since the beginning of 2017. The portfolio is 80% represented by bonds, a significant part of which is pledged under REPO transactions, and another 19% - "free" OFZ. Thus, on the one hand, investments in bonds are highly liquid, and on the other hand, the bank retains a reserve to increase its position to attract in the REPO market if necessary.
All interbank loans as of the reporting date were placed with commercial banks for short periods. In the interbank lending market, the financial institution shows high intra-month activity, including liquidity placement, although it acts mainly as a net borrower. The bank is also active in the foreign exchange market. In particular, in recent months, the turnover on the accounts of conversion transactions has risen to the level of 700-800 billion rubles.
According to the results of January-July 2017, the bank suffered a net loss in the amount of 272.1 million rubles. For the same period in 2016, the bank earned RUB 13.1 million in profit. For the whole of 2016, net profit amounted to 11.7 million rubles. The main pressure on the bank's financial result in 2017 comes from the cost of creating reserves in the second quarter.
Board of Directors: Grigory Gurevich (Chairman), Igor Fisenko, Sergey Shapoval, Olga Basalai, Dmitry Fominov.
Governing body: Olga Basalai (acting chairman), Tatyana Ovchinnikova (chief accountant), Artem Malenko, Elena Barenbaum.
* The Nobel Oil Group is an independent oil and gas holding specializing in the exploration and production of oil in the Timan-Pechora oil and gas province and in the territories of the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous Okrug. The holding was founded in 1998 and includes enterprises of various industries. The key enterprise of the group is CJSC NK Nobel Oil, which is engaged in the management of subsidiaries and affiliates, consulting activities for the development and design of fields. The main assets of the group include the oil producing enterprises of the Republic of Komi - CJSC "NeftUs" and CJSC "Kolvaneft", as well as several fields in the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug - Yugra. The holding group also includes ARM-Coating CJSC (a plant for applying protective coatings to the inner surface of oil pipes), Northern Transport Company LLC (transport services), Devon-invest LLC, Stati-neftegaz-invest LLC . The managing company of the holding is OOO Nobel Oil (KO). Since 2009, the group's shareholders have been an investment fundChina investment Corporation, a $300 billion asset manager and Hong Kong's leading investment groupOriental Patron. The president and main owner of the group is Grigory Gurevich, chairman of the board of directors of CJSC KB Rublev, a well-known oilman and former official who served as vice president of the Tyumen Oil Company (TNK) from 2000 to 2001.